Potential contribution of IL-7 to allergen-induced eosinophilic airway inflammation in asthma
- PMID: 19155487
- PMCID: PMC2851244
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.182.3.1404
Potential contribution of IL-7 to allergen-induced eosinophilic airway inflammation in asthma
Abstract
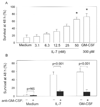
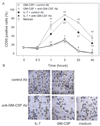
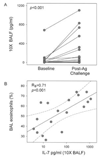
The primary function of IL-7 is to promote maturation and survival of T cells. Through microarray expression analysis, we previously observed that human blood eosinophils express mRNA for IL-7R alpha (CD127) and its common gamma chain (CD132). The purpose of this study was to determine whether eosinophils have functional IL-7 receptors and to assess the potential contribution of IL-7 to eosinophilic airway inflammation by evaluating its presence in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid of subjects with atopic asthma before and after segmental bronchoprovocation with allergen. Immunoblot analysis revealed that CD127 is present in highly purified human blood eosinophils. Furthermore, eosinophils responded to IL-7 with phosphorylation of STAT5, up-regulation of the activation marker CD69, and prolonged survival. Neutralization of GM-CSF but not IL-5 significantly blunted these functional responses, suggesting that IL-7 mediates its effects by promoting eosinophil release of autologous GM-CSF. Notably, the suppressive effect of anti-GM-CSF on STAT5 phosphorylation occurred within 10 min of eosinophil exposure to IL-7. Thus, IL-7 likely activates eosinophil release of preformed rather than newly synthesized GM-CSF. The biological relevance of IL-7 to eosinophilia in vivo was implicated in a study of airway allergen challenge in patients with allergic asthma. IL-7 concentrations in BAL fluid increased significantly 48 h after segmental allergen challenge and were highly correlated with BAL eosinophils (r = 0.7, p < 0.001). In conclusion, the airway response to allergen is associated with the generation of IL-7, which may contribute to airway inflammation by promoting enhanced eosinophil activation and survival. Activation of eosinophils is a novel function for IL-7.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures
The authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Giliani S, Mori L, de Saint BG, Le Deist F, Rodriguez-Perez C, Forino C, Mazzolari E, Dupuis S, Elhasid R, Kessel A, Galambrun C, Gil J, Fischer A, Etzioni A, Notarangelo LD. Interleukin-7 receptor alpha (IL-7Ralpha) deficiency: cellular and molecular bases. Analysis of clinical, immunological, and molecular features in 16 novel patients. Immunol. Rev. 2005;203:110–126. - PubMed
-
- Kovanen PE, Leonard WJ. Cytokines and immunodeficiency diseases: critical roles of the gamma(c)-dependent cytokines interleukins 2, 4, 7, 9, 15, and 21, and their signaling pathways. Immunol. Rev. 2004;202:67–83. - PubMed
-
- Guimond M, Fry TJ, Mackall CL. Cytokine signals in T-cell homeostasis. J Immunother. 2005;28:289–294. - PubMed
-
- Snyder KM, Mackall CL, Fry TJ. IL-7 in allogeneic transplant: clinical promise and potential pitfalls. Leuk. Lymphoma. 2006;47:1222–1228. - PubMed
-
- Nunnari G, Pomerantz RJ. IL-7 as a potential therapy for HIV-1-infected individuals. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2005;5:1421–1426. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

