Pleural tuberculosis in patients with early HIV infection is associated with increased TNF-alpha expression and necrosis in granulomas
- PMID: 19156215
- PMCID: PMC2626629
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004228
Pleural tuberculosis in patients with early HIV infection is associated with increased TNF-alpha expression and necrosis in granulomas
Abstract
Although granulomas may be an essential host response against persistent antigens, they are also associated with immunopathology. We investigated whether HIV co-infection affects histopathological appearance and cytokine profiles of pleural granulomas in patients with active pleural tuberculosis (TB). Granulomas were investigated in pleural biopsies from HIV positive and negative TB pleuritis patients. Granulomas were characterised as necrotic or non-necrotic, graded histologically and investigated for the mRNA expression of IL-12, IFN-gamma, TNF-alpha and IL-4 by in situ hybridisation. In all TB patients a mixed Th1/Th2 profile was noted. Necrotic granulomas were more evident in HIV positive patients with a clear association between TNF-alpha and necrosis. This study demonstrates immune dysregulation which may include TNF-alpha-mediated immunopathology at the site of disease in HIV infected pleural TB patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
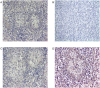

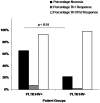
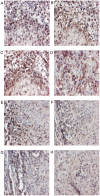
References
-
- Algood HM, Chan J, Flynn JL. Chemokines and tuberculosis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2003;14:467–477. - PubMed
-
- Thurlbeck W, Churg A. Chapter 13: Pathology of the Lung. Thieme Medical Publishers; 1995. p. 234.
-
- Hasleton PS. Chapter 7: Spencer's Pathology of the Lung. Mc Graw-Hill; 1996. p. 227.
-
- Ellner JJ, Barnes PF, Wallis RS, Modlin RL. The immunology of tuberculous pleurisy. Semin Respir Infect. 1988;3:335–342. - PubMed
-
- Roper WH, Waring JJ. Primary serofibrinous pleural effusion in military personnel. Am Rev Tuberc. 1955;71:616–634. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

