Integrated signaling in heterodimers and receptor mosaics of different types of GPCRs of the forebrain: relevance for schizophrenia
- PMID: 19156349
- PMCID: PMC2953764
- DOI: 10.1007/s00702-008-0174-9
Integrated signaling in heterodimers and receptor mosaics of different types of GPCRs of the forebrain: relevance for schizophrenia
Abstract
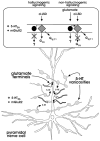
Receptor-receptor interactions within receptor heterodimers and receptor mosaics formed by different types of GPCRs represent an important integrative mechanism for signaling in brain networks at the level of the plasma membrane. The malfunction of special heterodimers and receptor mosaics in the ventral striatum containing D(2) receptors and 5-HT(2A) receptors in cortical networks may contribute to disturbances of key pathways involving ventral striato-pallidal GABA neurons and mediodorsal thalamic prefrontal glutamate neurons that may lead to the development of schizophrenia. The ventral striatum transmits emotional information to the cerebral cortex through a D(2) regulated accumbal-ventral pallidal-mediodorsal-prefrontal circuit which is of special interest to schizophrenia in view of the reduced number of glutamate mediodorsal-prefrontal projections associated with this disease. This circuit is especially vulnerable to D(2) receptor activity in the nucleus accumbens, since it produces a reduction in the prefrontal glutamate drive from the mediodorsal nucleus. The following D(2) receptor containing heterodimers/receptor mosaics are of special interest to schizophrenia: A(2A)-D(2), mGluR5-D(2), CB(1)-D(2), NTS(1)-D(2) and D(2)-D(3) and are discussed in this review. They may have a differential distribution pattern in the local circuits of the ventral striato-pallidal GABA pathway, predominantly located extrasynaptically. Specifically, trimeric receptor mosaics consisting of A(2A)-D(2)-mGluR5 and CB(1)-D(2)-A(2A) may also exist in these local circuits and are discussed. The integration of receptor signaling within assembled heterodimers/receptor mosaics is brought about by agonists and allosteric modulators. These cause the intramembrane receptor-receptor interactions, via allosteric mechanisms, to produce conformational changes that pass over the receptor interfaces. Exogenous and endogenous cooperativity is discussed as well as the role of the cortical mGluR2-5-HT(2A) heterodimer/receptor mosaic in schizophrenia (Gonzalez-Maeso et al. 2008). Receptor-receptor interactions within receptor heterodimer/receptor mosaics of different receptors in the ventral striatum and cerebral cortex give novel strategies for treatment of schizophrenia involving, e.g., monotherapy with either A(2A), mGluR5, CB(1) or NTS(1) agonists or combined therapies with some of these agonists combined with D(2)-like antagonists that specifically target the ventral striatum. In addition, a combined targeting of receptor mosaics in the ventral striatum and in the cerebral cortex should also be considered.
Figures

References
-
- Aghajanian GK, Marek GJ. Serotonin model of schizophrenia: emerging role of glutamate mechanisms. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2000;31:302–312. - PubMed
-
- Aghajanian GK, Foote WE, Sheard MH. Lysergic acid diethylamide: sensitive neuronal units in the midbrain raphe. Science. 1968;161:706–708. - PubMed
-
- Agnati LF, Fuxe K, Benfenati F, Battistini N. Neurotensin in vitro markedly reduces the affinity in subcortical limbic 3H-N-propylnorapomorphine binding sites. Acta Physiol Scand. 1983;119:459–461. - PubMed
-
- Agnati LF, Ferre S, Lluis C, Franco R, Fuxe K. Molecular mechanisms and therapeutical implications of intramembrane receptor/receptor interactions among heptahelical receptors with examples from the striatopallidal GABA neurons. Pharmacol Rev. 2003;55:509–550. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

