Myelin-associated glycoprotein and its axonal receptors
- PMID: 19156870
- PMCID: PMC2892843
- DOI: 10.1002/jnr.21992
Myelin-associated glycoprotein and its axonal receptors
Abstract
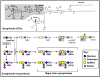
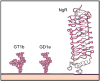
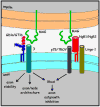
Myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) is expressed on the innermost myelin membrane wrap, directly apposed to the axon surface. Although it is not required for myelination, MAG enhances long-term axon-myelin stability, helps to structure nodes of Ranvier, and regulates the axon cytoskeleton. In addition to its role in axon-myelin stabilization, MAG inhibits axon regeneration after injury; MAG and a discrete set of other molecules on residual myelin membranes at injury sites actively signal axons to halt elongation. Both the stabilizing and the axon outgrowth inhibitory effects of MAG are mediated by complementary MAG receptors on the axon surface. Two MAG receptor families have been described, sialoglycans (specifically gangliosides GD1a and GT1b) and Nogo receptors (NgRs). Controversies remain about which receptor(s) mediates which of MAG's biological effects. Here we review the findings and challenges in associating MAG's biological effects with specific receptors.
Figures
References
-
- Atwal JK, Pinkston-Gosse J, Syken J, Stawicki S, Wu Y, Shatz C, Tessier-Lavigne M. PirB is a functional receptor for myelin inhibitors of axonal regeneration. Science. 2008;322:967–970. - PubMed
-
- Bartsch S, Montag D, Schachner M, Bartsch U. Increased number of unmyelinated axons in optic nerves of adult mice deficient in the myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) Brain Res. 1997;762:231–234. - PubMed
-
- Bartsch U, Kirchhoff F, Schachner M. Immunohistological localization of the adhesion molecules L1, N-CAM, and MAG in the developing and adult optic nerve of mice. J Comp Neurol. 1989;284:451–462. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

