Role of alpha2-adrenoceptors and glutamate mechanisms in the external urethral sphincter continence reflex in rats
- PMID: 19157445
- PMCID: PMC2649991
- DOI: 10.1016/j.juro.2008.11.008
Role of alpha2-adrenoceptors and glutamate mechanisms in the external urethral sphincter continence reflex in rats
Abstract
Purpose: We investigated the role of alpha(2)-adrenoceptors and glutamate mechanisms in the urethral continence reflex in response to abdominal pressure increases.
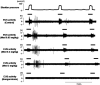
Materials and methods: Under urethane anesthesia external urethral sphincter electromyogram activity was evaluated in spinal cord transected (T8-T9) female rats during lower abdominal wall compression before and after intravenous application of test drugs. The effects of the N-methyl-D-aspartate glutamate receptor antagonist MK-801 (Sigma) or the alpha(2)-adrenoceptor agonist medetomidine (Tocris Cookson, Ellisville, Missouri) (each 0.03, 0.3 and 3 mg/kg intravenously) on external urethral sphincter activity were examined. A 0.3 mg/kg intravenous dose of the alpha(2)-adrenoceptor antagonist idazoxan (Sigma) was then administered before or after the application of 1 mg/kg MK-801 intravenously. In addition, 0.3 mg/kg idazoxan were administered intravenously following the application of 1 mg/kg of the serotonin/norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor duloxetine (Kemprotec, Middlesbrough, United Kingdom) intravenously.
Results: MK-801 and medetomidine dose dependently decreased external urethral sphincter activity. Idazoxan significantly increased external urethral sphincter activity by 64% but the increase in activity after idazoxan was abolished by MK-801. On the other hand, idazoxan did not reverse the inhibitory effects of MK-801. In addition, idazoxan significantly potentiated the duloxetine effects on external urethral sphincter activity by 120%.
Conclusions: These results indicate that 1) glutamate is a major excitatory neurotransmitter in the urethral continence reflex response to abdominal pressure increases, 2) alpha(2)-adrenoceptor activation suppresses external urethral sphincter activity, probably via presynaptic inhibition of glutamate release and 3) the effects of serotonin/norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors are enhanced by alpha(2)-adrenoceptor inhibition. Therefore, alpha(2)-adrenoceptor antagonists could be beneficial for treating stress urinary incontinence.
Figures
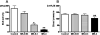
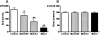



Similar articles
-
Alpha2-adrenoceptor blockade potentiates the effect of duloxetine on sneeze induced urethral continence reflex in rats.J Urol. 2010 Aug;184(2):762-8. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2010.03.106. Epub 2010 Jun 19. J Urol. 2010. PMID: 20639053 Free PMC article.
-
Noradrenergic Mechanisms Controlling Urethral Smooth and Striated Muscle Function in Urethral Continence Reflex in Rats.Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2015 Sep;7(3):155-61. doi: 10.1111/luts.12065. Epub 2014 Jul 7. Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2015. PMID: 26663731
-
Effect of duloxetine, a norepinephrine and serotonin reuptake inhibitor, on sneeze-induced urethral continence reflex in rats.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008 Jul;295(1):F264-71. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.90241.2008. Epub 2008 May 14. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18480175 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonin and norepinephrine involvement in efferent pathways to the urethral rhabdosphincter: implications for treating stress urinary incontinence.Urology. 2003 Oct;62(4 Suppl 1):3-9. doi: 10.1016/s0090-4295(03)00754-4. Urology. 2003. PMID: 14550831 Review.
-
Neurophysiology and therapeutic receptor targets for stress urinary incontinence.Int J Urol. 2012 Jun;19(6):524-37. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2012.02976.x. Epub 2012 Mar 9. Int J Urol. 2012. PMID: 22404481 Review.
Cited by
-
α(2)-Adrenoceptors as a new target for stress urinary incontinence.Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2009 Sep 1;1(s1):S26-S29. doi: 10.1111/j.1757-5672.2009.00023.x. Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2009. PMID: 21151772 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Alpha2-adrenoceptor blockade potentiates the effect of duloxetine on sneeze induced urethral continence reflex in rats.J Urol. 2010 Aug;184(2):762-8. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2010.03.106. Epub 2010 Jun 19. J Urol. 2010. PMID: 20639053 Free PMC article.
-
Role of 5-HT1A receptors in control of lower urinary tract function in anesthetized rats.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010 Mar;298(3):F771-8. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00266.2009. Epub 2009 Dec 30. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20042459 Free PMC article.
-
Coadministration of low-dose serotonin/noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) duloxetine with α 2-adrenoceptor blockers to treat both female and male mild-to-moderate stress urinary incontinence (SUI).G Chir. 2013 Jul-Aug;34(7-8):189-94. doi: 10.11138/gchir/2013.34.7.189. G Chir. 2013. PMID: 24091172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neural control of the female urethral and anal rhabdosphincters and pelvic floor muscles.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010 Aug;299(2):R416-38. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00111.2010. Epub 2010 May 19. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20484700 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Norton P, Brubaker L. Urinary incontinence in women. Lancet. 2006;367:57. - PubMed
-
- Kamo I, Kaiho Y, Canon TW, Chancellor MB, de Groat WC, Prantil RL, et al. Functional analysis of active urethral closure mechanisms under sneeze induced stress condition in a rat model of birth trauma. J Urol. 2006;176:2711. - PubMed
-
- Kamo I, Cannon TW, Conway DA, Torimoto K, Chancellor MB, de Groat WC, et al. The role of bladder-to-urethral reflexes in urinary continence mechanisms in rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2004;287:F434. - PubMed
-
- Kernan WN, Viscoli CM, Brass LM, Broderick JP, Brott T, Feldmann E, et al. Phenylpropanolamine and the risk of hemorrhagic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:1826. - PubMed
-
- Danuser H, Bemis K, Thor KB. Pharmacological analysis of the noradrenergic control of central sympathetic and somatic reflexes controlling the lower urinary tract in the anesthetized cat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995;274:820. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

