Detection of WU polyomavirus DNA by real-time PCR in nasopharyngeal aspirates, serum, and stool samples
- PMID: 19157970
- PMCID: PMC7172993
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcv.2008.12.004
Detection of WU polyomavirus DNA by real-time PCR in nasopharyngeal aspirates, serum, and stool samples
Abstract
Background: The human WU polyomavirus (WUPyV) has been recently described as a novel virus in respiratory tract samples.
Objective: To investigate the viral load of WUPyV in nasopharyngeal aspirates (NPAs), stool, and serum samples of pediatric patients with acute respiratory tract diseases.
Study design: We established a real-time PCR for WUPyV DNA and tested NPA obtained between 2002 and 2007 from pediatric in-patients with acute respiratory tract diseases. In addition, 14 stool and 14 serum samples of children with WUPyV DNA positive NPA were analysed.
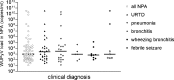
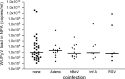
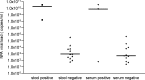
Results: WUPyV DNA was found in 5.2% of 1232 NPA. The median viral load in the NPA was 950 copies/ml (maximum 3.4 x 10(10) copies/ml). The WUPyV load in NPA was neither associated with the coinfection status nor with the clinical diagnoses. WUPyV DNA was found in 3 of 14 serum samples and in 2 of 14 stool samples. The WUPyV load in NPA tended to be higher in viremic children.
Conclusion: WUPyV DNA was found in NPA, serum, and stool of hospitalised children with acute respiratory tract diseases. Further studies are necessary to determine whether WUPyV is a human pathogen.
Figures
References
-
- Fouchier R.A., Rimmelzwaan G.F., Kuiken T., Osterhaus A.D. Newer respiratory virus infections: human metapneumovirus, avian influenza virus, and human coronaviruses. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2005;18:141–146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

