HDAC6 modulates Hsp90 chaperone activity and regulates activation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling
- PMID: 19158084
- PMCID: PMC2658039
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M808999200
HDAC6 modulates Hsp90 chaperone activity and regulates activation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling
Retraction in
-
Withdrawal: HDAC6 modulates Hsp90 chaperone activity and regulates activation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jan 3;295(1):297. doi: 10.1074/jbc.W119.012142. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 31900379 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
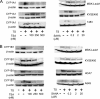
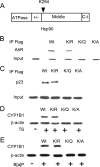
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), a ligand-activated member of the basic helix-loop-helix family of transcription factors, binds with high affinity to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) and the environmental toxin 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (dioxin). Most of the biochemical, biological, and toxicological responses caused by exposure to PAHs and polychlorinated dioxins are mediated, at least in part, by the AhR. The AhR is a client protein of Hsp90, a molecular chaperone that can be reversibly acetylated with functional consequences. The main objective of this study was to determine whether modulating Hsp90 acetylation would affect ligand-mediated activation of AhR signaling. Trichostatin A and suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, two broad spectrum HDAC inhibitors, blocked PAH and dioxin-mediated induction of CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 in cell lines derived from the human aerodigestive tract. Silencing HDAC6 or treatment with tubacin, a pharmacological inhibitor of HDAC6, also suppressed the induction of CYP1A1 and CYP1B1. Inhibiting HDAC6 led to hyperacetylation of Hsp90 and loss of complex formation with AhR, cochaperone p23, and XAP-2. Inactivation or silencing of HDAC6 also led to reduced binding of ligand to the AhR and decreased translocation of the AhR from cytosol to nucleus in response to ligand. Ligand-induced recruitment of the AhR to the CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 promoters was inhibited when HDAC6 was inactivated. Mutation analysis of Hsp90 Lys(294) shows that its acetylation status is a strong determinant of interactions with AhR and p23 in addition to ligand-mediated activation of AhR signaling. Collectively, these results show that HDAC6 activity regulates the acetylation of Hsp90, the ability of Hsp90 to chaperone the AhR, and the expression of AhR-dependent genes. Given the established link between activation of AhR signaling and xenobiotic metabolism, inhibitors of HDAC6 may alter drug or carcinogen metabolism.
Figures
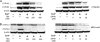






Comment in
-
Findings of Research Misconduct.Fed Regist. 2023 Sep 13;88(176):62800-62803. Fed Regist. 2023. PMID: 37736072 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Findings of Research Misconduct.Fed Regist. 2023 Sep 13;88(176):62803-62807. Fed Regist. 2023. PMID: 37736073 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Gu, Y. Z., Hogenesch, J. B., and Bradfield, C. A. (2000) Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 40 519–561 - PubMed
-
- Poland, A., Glover, E., and Kende, A. S. (1976) J. Biol. Chem. 251 4936–4946 - PubMed
-
- Bock, K. W., and Köhle, C. (2006) Biochem. Pharmacol. 72 393–404 - PubMed
-
- Moennikes, O., Loeppen, S., Buchmann, A., Andersson, P., Ittrich, C., Poellinger, L., and Schwarz, M. (2004) Cancer Res. 64 4707–4710 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

