Performance of microcalorimetry for early detection of methicillin resistance in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 19158262
- PMCID: PMC2650961
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02374-08
Performance of microcalorimetry for early detection of methicillin resistance in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
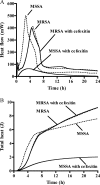
We describe a calorimetric assay for the detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) within 5 h. Microbial heat was calculated in culture with and without cefoxitin. Among 30 genetically distinct clinical isolates, 19/20 MRSA (95%) and 10/10 methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus (100%) were correctly identified. Microcalorimetry may be useful for rapid MRSA screening.
Figures

References
-
- Amsterdam, D. 2005. Susceptibility testing of antimicrobials in liquid media, p. 61-143. In V. Lorian (ed.), Antibiotics in laboratory medicine, 5th ed. LWW Press, Philadelphia, PA.
-
- Brown, D. F., D. I. Edwards, P. M. Hawkey, D. Morrison, G. L. Ridgway, K. J. Towner, and M. W. Wren. 2005. Guidelines for the laboratory diagnosis and susceptibility testing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 561000-1018. - PubMed
-
- Felten, A., B. Grandry, P. H. Lagrange, and I. Casin. 2002. Evaluation of three techniques for detection of low-level methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): a disk diffusion method with cefoxitin and moxalactam, the Vitek 2 system, and the MRSA-screen latex agglutination test. J. Clin. Microbiol. 402766-2771. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mackenzie, A. M., H. Richardson, R. Lannigan, and D. Wood. 1995. Evidence that the National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards disk test is less sensitive than the screen plate for detection of low-expression-class methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 331909-1911. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

