Clinical and microbiological characteristics of severe Streptococcus pyogenes disease in Europe
- PMID: 19158266
- PMCID: PMC2668334
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02155-08
Clinical and microbiological characteristics of severe Streptococcus pyogenes disease in Europe
Abstract
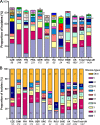
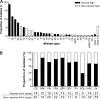
In an attempt to compare the epidemiology of severe Streptococcus pyogenes infection within Europe, prospective data were collected through the Strep-EURO program. Surveillance for severe cases of S. pyogenes infection diagnosed during 2003 and 2004 was undertaken in 11 countries across Europe by using a standardized case definition and questionnaire. Patient data as well as bacterial isolates were collected and characterized by T and M/emm typing, and selected strains were analyzed for the presence of superantigen genes. Data were analyzed to compare the clinical and microbiological patterns of the infections across the participating countries. A total of 4,353 isolates were collected from 5,521 cases with severe S. pyogenes infections who were identified. A wide diversity of M/emm types (n = 104) was found among the S. pyogenes clinical isolates, but the M/emm type distribution varied broadly between participating countries. The 10 most predominant M/emm types were M/emm type 1 (M/emm1), M/emm28, M/emm3, M/emm89, M/emm87, M/emm12, M/emm4, M/emm83, M/emm81, and M/emm5, in descending order. A correlation was found between some specific disease manifestations, the age of the patients, and the emm types. Although streptococcal toxic shock syndrome and necrotizing fasciitis were caused by a large number of types, they were particularly associated with M/emm1 and M/emm3. The emm types included in the 26-valent vaccine under development were generally well represented in the present material; 16 of the vaccine types accounted for 69% of isolates. The Strep-EURO collaborative program has contributed to enhancement of the knowledge of the spread of invasive disease caused by S. pyogenes within Europe and encourages future surveillance by the notification of cases and the characterization of strains, which are important for vaccination strategies and other health care issues.
Figures

References
-
- Aguiar, S. I., I. Serrano, F. R. Pinto, J. Melo-Cristino, and M. Ramirez. 2008. Changes in Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes causing invasive disease with non-universal vaccination coverage of the seven-valent conjugate vaccine. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 14835-843. - PubMed
-
- Areschoug, T., F. Carlsson, M. Stalhammar-Carlemalm, and G. Lindahl. 2004. Host-pathogen interactions in Streptococcus pyogenes infections, with special reference to puerperal fever and a comment on vaccine development. Vaccine 22(Suppl. 1)S9-S14. - PubMed
-
- Beachey, E. H., and J. M. Seyer. 1986. Protective and nonprotective epitopes of chemically synthesized peptides of the NH2-terminal region of type 6 streptococcal M protein. J. Immunol. 1362287-2292. - PubMed
-
- Beachey, E. H., J. M. Seyer, J. B. Dale, W. A. Simpson, and A. H. Kang. 1981. Type-specific protective immunity evoked by synthetic peptide of Streptococcus pyogenes M protein. Nature 292457-459. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

