Spatiotemporal patterns of cortical activity with bilateral cochlear implants in congenital deafness
- PMID: 19158306
- PMCID: PMC6665161
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2424-08.2009
Spatiotemporal patterns of cortical activity with bilateral cochlear implants in congenital deafness
Abstract
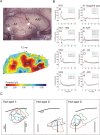
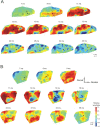
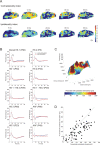
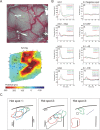
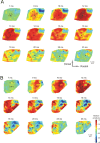
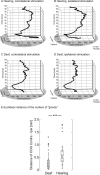
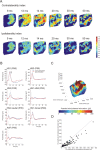
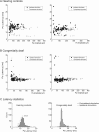
Congenital deafness affects developmental processes in the auditory cortex. In this study, local field potentials (LFPs) were mapped at the cortical surface with microelectrodes in response to cochlear implant stimulation. LFPs were compared between hearing controls and congenitally deaf cats (CDCs). Pulsatile electrical stimulation initially evoked cortical activity in the rostral parts of the primary auditory field (A1). This progressed both in the approximate dorsoventral direction (along the isofrequency stripe) and in the rostrocaudal direction. The dorsal branch of the wavefront split into a caudal branch (propagating in A1) and another smaller one propagating rostrally into the AAF (anterior auditory field). After the front reached the caudal border of A1, a "reflection wave" appeared, propagating back rostrally. In total, the waves took approximately 13-15 ms to propagate along A1 and return back. In CDCs, the propagation pattern was significantly disturbed, with a more synchronous activation of distant cortical regions. The maps obtained from contralateral and ipsilateral stimulation overlapped in both groups of animals. Although controls showed differences in the latency-amplitude patterns, cortical waves evoked by contralateral and ipsilateral stimulation were more similar in CDCs. Additionally, in controls, LFPs with contralateral and ipsilateral stimulation were more similar in caudal A1 than in rostral A1. This dichotomy was lost in deaf animals. In conclusion, propagating cortical waves are specific for the contralateral ear, they are affected by auditory deprivation, and the specificity of the cortex for stimulation of the contralateral ear is reduced by deprivation.
Figures


References
-
- Arieli A, Sterkin A, Grinvald A, Aertsen A. Dynamics of ongoing activity: explanation of the large variability in evoked cortical responses. Science. 1996;273:1868–1871. - PubMed
-
- Behrendt M. Entwicklung und Herstellung eines Cochlea-Implantates zur chronischen Stimulation von gehörlosen weißen Katzen. Frankfurt am Main, Germany: J. W. Goethe University; 1999.
-
- Bierer JA, Middlebrooks JC. Auditory cortical images of cochlear-implant stimuli: dependence on electrode configuration. J Neurophysiol. 2002;87:478–492. - PubMed
-
- Bozhko GT, Slepchenko AF. Functional organization of the callosal connections of the cat auditory cortex. Neurosci Behav Physiol. 1988;18:323–330. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
