Phospholemman regulates cardiac Na+/Ca2+ exchanger by interacting with the exchanger's proximal linker domain
- PMID: 19158404
- PMCID: PMC2670646
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00196.2008
Phospholemman regulates cardiac Na+/Ca2+ exchanger by interacting with the exchanger's proximal linker domain
Abstract
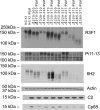
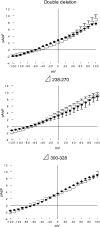
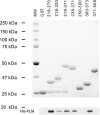
Phospholemman (PLM) belongs to the FXYD family of small ion transport regulators. When phosphorylated at Ser(68), PLM inhibits cardiac Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger (NCX1). We previously demonstrated that the cytoplasmic tail of PLM interacts with the proximal intracellular loop (residues 218-358), but not the transmembrane (residues 1-217 and 765-938) or Ca(2+)-binding (residues 371-508) domains, of NCX1. In this study, we used intact Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger with various deletions in the intracellular loop to map the interaction sites with PLM. We first demonstrated by Western blotting and confocal immunofluorescence microscopy that wild-type (WT) NCX1 and its deletion mutants were expressed in transfected HEK-293 cells. Cotransfection with PLM and NCX1 (or its deletion mutants) in HEK-293 cells did not decrease expression of NCX1 (or its deletion mutants). Coexpression of PLM with WT NCX1 inhibited NCX1 current (I(NaCa)). Deletion of residues 240-679, 265-373, 250-300, or 300-373 from WT NCX1 resulted in loss of inhibition of I(NaCa) by PLM. Inhibition of I(NaCa) by PLM was preserved when residues 229-237, 270-300, 328-330, or 330-373 were deleted from the intracellular loop of NCX1. These results suggest that PLM mediated inhibition of I(NaCa) by interacting with two distinct regions (residues 238-270 and 300-328) of NCX1. Indeed, I(NaCa) measured in mutants lacking residues 238-270, 300-328, or 238-270 + 300-328 was not affected by PLM. Glutathione S-transferase pull-down assays confirmed that PLM bound to fragments corresponding to residues 218-371, 218-320, 218-270, 238-371, and 300-373, but not to fragments encompassing residues 250-300 and 371-508 of NCX1, indicating that residues 218-270 and 300-373 physically associated with PLM. Finally, acute regulation of I(NaCa) by PLM phosphorylation observed with WT NCX1 was absent in 250-300 deletion mutant but preserved in 229-237 deletion mutant. We conclude that PLM mediates its inhibition of NCX1 by interacting with residues 238-270 and 300-328.
Figures





References
-
- Ahlers BA, Zhang XQ, Moorman JR, Rothblum LI, Carl LL, Song J, Wang J, Geddis LM, Tucker AL, Mounsey JP, Cheung JY. Identification of an endogenous inhibitor of the cardiac Na+/Ca2+ exchanger, phospholemman. J Biol Chem 280: 19875–19882, 2005. - PubMed
-
- Bers DM Cardiac excitation-contraction coupling. Nature 415: 198–205, 2002. - PubMed
-
- Bossuyt J, Ai X, Moorman JR, Pogwizd SM, Bers DM. Expression and phosphorylation of the Na-pump regulatory subunit phospholemman in heart failure. Circ Res 97: 558–565, 2005. - PubMed
-
- Bossuyt J, Despa S, Martin JL, Bers DM. Phospholemman phosphorylation alters its fluorescence resonance energy transfer with the Na/K-ATPase pump. J Biol Chem 281: 32765–32773, 2006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

