AIM2 recognizes cytosolic dsDNA and forms a caspase-1-activating inflammasome with ASC
- PMID: 19158675
- PMCID: PMC2726264
- DOI: 10.1038/nature07725
AIM2 recognizes cytosolic dsDNA and forms a caspase-1-activating inflammasome with ASC
Abstract
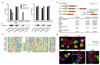
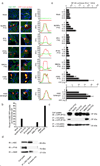
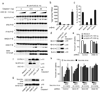
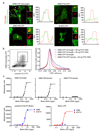
The innate immune system senses nucleic acids by germline-encoded pattern recognition receptors. RNA is sensed by Toll-like receptor members TLR3, TLR7 and TLR8, or by the RNA helicases RIG-I (also known as DDX58) and MDA-5 (IFIH1). Little is known about sensors for cytoplasmic DNA that trigger antiviral and/or inflammatory responses. The best characterized of these responses involves activation of the TANK-binding kinase (TBK1)-interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) signalling axis to trigger transcriptional induction of type I interferon genes. A second, less well-defined pathway leads to the activation of an 'inflammasome' that, via caspase-1, controls the catalytic cleavage of the pro-forms of the cytokines IL1beta and IL18 (refs 6, 7). Using mouse and human cells, here we identify the PYHIN (pyrin and HIN domain-containing protein) family member absent in melanoma 2 (AIM2) as a receptor for cytosolic DNA, which regulates caspase-1. The HIN200 domain of AIM2 binds to DNA, whereas the pyrin domain (but not that of the other PYHIN family members) associates with the adaptor molecule ASC (apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase activation and recruitment domain) to activate both NF-kappaB and caspase-1. Knockdown of Aim2 abrogates caspase-1 activation in response to cytoplasmic double-stranded DNA and the double-stranded DNA vaccinia virus. Collectively, these observations identify AIM2 as a new receptor for cytoplasmic DNA, which forms an inflammasome with the ligand and ASC to activate caspase-1.
Figures
References
-
- Meylan E, Tschopp J, Karin M. Intracellular pattern recognition receptors in the host response. Nature. 2006;442(7098):39. - PubMed
-
- Ishii KJ, et al. A Toll-like receptor-independent antiviral response induced by double-stranded B-form DNA. Nat Immunol. 2006;7(1):40. - PubMed
-
- Stetson DB, Medzhitov R. Recognition of cytosolic DNA activates an IRF3-dependent innate immune response. Immunity. 2006;24(1):93. - PubMed
-
- Takaoka A, et al. DAI (DLM-1/ZBP1) is a cytosolic DNA sensor and an activator of innate immune response. Nature. 2007;448(7152):501. - PubMed
-
- Ishii KJ, et al. TANK-binding kinase-1 delineates innate and adaptive immune responses to DNA vaccines. Nature. 2008;451(7179):725. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

