Overexpression of CERKL, a gene responsible for retinitis pigmentosa in humans, protects cells from apoptosis induced by oxidative stress
- PMID: 19158957
- PMCID: PMC2628313
Overexpression of CERKL, a gene responsible for retinitis pigmentosa in humans, protects cells from apoptosis induced by oxidative stress
Abstract
Purpose: Retinitis pigmentosa (RP), a retinal neurodegenerative disorder characterized by apoptosis of photoreceptor cells, is caused by mutations in many different genes. We analyzed the RP gene ceramide kinase-like (CERKL) to determine CERKL function and contribution to pathogenesis.
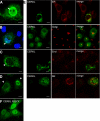
Methods: RT-PCR was performed to characterize CERKL expression in many human adult and fetal tissues, including retina. We analyzed the protein subcellular localization by confocal microscopy and further verified it by sucrose gradients. We performed lipid kinase activity assays. And finally, we studied the effects on cell apoptosis after CERKL overexpression in transiently transfected cultured cells by propidium iodide staining and poly-(ADP-ribose)-polymerase (PARP) caspase-dependent cleavage.
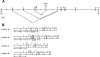
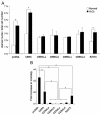
Results: CERKL transcripts underwent alternative splicing. In the human retina, four different CERKL isoforms of 532, 558, 419, and 463 amino acids were expressed. CERKL proteins were mainly localized in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi compartments, but they also shifted localization to nuclei and nucleoli. We also found that CERKL prevented cells from entering apoptosis induced by oxidative-stress conditions.
Conclusions: CERKL remains a unique orphan lipid kinase in that no candidate substrate has been identified after intense research. The dynamic localization of CERKL suggests multiple sites of action. Remarkably, CERKL (but not the RP R257X mutant) exerts a protective role in cells against oxidative stress, consistent with RP mutations impairing the normal protein function in photoreceptors and thus tilting the balance toward apoptosis. These results provide valuable insights into the molecular mechanisms causing retinal degeneration.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Molecular Mechanisms Related to Oxidative Stress in Retinitis Pigmentosa.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 May 26;10(6):848. doi: 10.3390/antiox10060848. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34073310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of a ceramide kinase-like protein.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005 Feb 21;1687(1-3):31-43. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2004.11.012. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005. PMID: 15708351
-
Spatiotemporal expression pattern of ceramide kinase-like in the mouse retina.Mol Vis. 2010 Dec 3;16:2539-49. Mol Vis. 2010. PMID: 21151604 Free PMC article.
-
pVHL interacts with Ceramide kinase like (CERKL) protein and ubiquitinates it for oxygen dependent proteasomal degradation.Cell Signal. 2015 Nov;27(11):2314-23. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2015.08.011. Epub 2015 Aug 18. Cell Signal. 2015. PMID: 26296657
-
Oxidative Stress and Microglial Response in Retinitis Pigmentosa.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 28;21(19):7170. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197170. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32998461 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomic analysis of the liver in aged laying hens with different intensity of brown eggshell color.Anim Biosci. 2021 May;34(5):811-823. doi: 10.5713/ajas.20.0237. Epub 2020 Oct 13. Anim Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33152221 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms Related to Oxidative Stress in Retinitis Pigmentosa.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 May 26;10(6):848. doi: 10.3390/antiox10060848. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34073310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CERKL, a retinal disease gene, encodes an mRNA-binding protein that localizes in compact and untranslated mRNPs associated with microtubules.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 3;9(2):e87898. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087898. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24498393 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated differential transcriptome maps of Acute Megakaryoblastic Leukemia (AMKL) in children with or without Down Syndrome (DS).BMC Med Genomics. 2014 Dec 5;7:63. doi: 10.1186/s12920-014-0063-z. BMC Med Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25476127 Free PMC article.
-
CERKL knockdown causes retinal degeneration in zebrafish.PLoS One. 2013 May 9;8(5):e64048. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064048. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23671706 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Auslender N, Sharon D, Abbasi AH, Garzozi HJ, Banin E, Ben-Yosef T. A common founder mutation of CERKL underlies autosomal recessive retinal degeneration with early macular involvement among Yemenite Jews. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007;48:5431–8. - PubMed
-
- Hannun YA, Obeid LM. The ceramide-centric universe of lipid-mediated cell regulation: stress encounters of the lipid kind. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:25847–50. - PubMed
-
- Hannun YA, Obeid LM. Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: lessons from sphingolipids. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:139–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
