Cooling therapy for acute stroke
- PMID: 19160194
- PMCID: PMC7073930
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001247.pub2
Cooling therapy for acute stroke
Abstract
Background: Increased body temperatures are common in patients with acute stroke and are associated with poor outcome. In animal models of focal cerebral ischaemia, temperature-lowering therapy reduces infarct volume. In patients with acute stroke, lowering temperature may therefore improve outcome. This is an update of a Cochrane review first published in 1999.
Objectives: To assess the effects of pharmacological and physical strategies to reduce body or brain temperature in patients with acute stroke.
Search strategy: We searched the Cochrane Stroke Group trials register (last searched December 2007). In addition, we searched MEDLINE and EMBASE (January 1998 to December 2007). We scanned references and contacted authors of included trials. For the previous version of this review, the authors contacted pharmaceutical companies and manufactures of cooling equipment in this field.
Selection criteria: We considered all completed randomised or non-randomised controlled clinical trials, published or unpublished, where pharmacological or physical strategies or both to reduce temperature were applied in patients with acute ischaemic stroke or intracerebral haemorrhage. Outcome measures were death or dependency (modified Rankin Scale score >/= 3) at the end of follow up, and adverse effects.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently applied the inclusion criteria, assessed trial quality, and extracted and cross-checked the data.
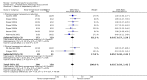
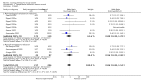
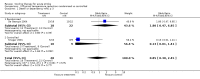
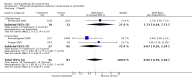
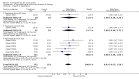
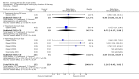
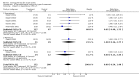
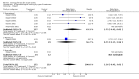
Main results: We included five pharmacological temperature reduction trials and three physical cooling trials involving a total of 423 participants. We found no statistically significant effect of pharmacological or physical temperature-lowering therapy in reducing the risk of death or dependency (odds ratio (OR) 0.9, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.6 to 1.4) or death (OR 0.9, 95% CI 0.5 to 1.5). Both interventions were associated with a non-significant increase in the occurrence of infections.
Authors' conclusions: There is currently no evidence from randomised trials to support routine use of physical or pharmacological strategies to reduce temperature in patients with acute stroke. Large randomised clinical trials are needed to study the effect of such strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
Heleen M den Hertog is the study co‐ordinator of the ongoing PAIS trial. Dr Diederik WJ Dippel and Dr H Bart van der Worp were principal investigators of the PAPAS and PISA trials included in this review and of the ongoing PAIS trial. All the analyses and the interpretations reflect the opinions of the authors. No commercial organisation or other party was involved in the analysis or interpretation of data or in writing this review.
Figures


Update of
-
Cooling therapy for acute stroke.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000;(2):CD001247. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001247. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009 Jan 21;(1):CD001247. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001247.pub2. PMID: 10796427 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Castillo 2003 {unpublished data only}
-
- Castillo J, Ortiz P, Ruiz J, Puerta JL. A randomized multicentre double blind clinical trial of metamizole 2g/8h, iv ampoules versus placebo every 8h iv ampoules, administered during 3 days consecutively as antithermic therapy in the acute phase of ischemic stroke. A 30 day study (ATIS study). Unpublished.
De Georgia 2004 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Georgia MA, Krieger DW, Abou‐Chebl A, Devlin TG, Jauss M, Davis SM, et al. Cooling for acute ischemic stroke brain damage (COOLAID). Neurology 2004;63:312‐7. - PubMed
Dippel 2001a {published and unpublished data}
-
- Dippel DWJ, Breda EJ, Gemert HMA, Worp HB, Meijer RJ, Kappelle LJ, et al. Effect of paracetamol (acetaminophen) on body temperature in acute ischemic stroke: a double blind, randomized phase II clinical trial. Stroke 2001;32:1607‐12. - PubMed
Dippel 2001b {published and unpublished data}
-
- Dippel DWJ, Breda EJ, Gemert HMA, Worp HB, Meijer RJ, Kappelle LJ, et al. Effect of paracetamol (acetaminophen) on body temperature in acute ischemic stroke: a double blind, randomized phase II clinical trial. Stroke 2001;32:1607‐12. - PubMed
Dippel 2003a {published data only}
Dippel 2003b {published and unpublished data}
Kammersgaard 2000 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Kammersgaard LP, Rasmussen BH, Jorgensen HS, Reith J, Weber U, Olsen TS. Feasibility and safety of inducing modest hypothermia in awake patients with acute stroke through surface cooling: a case‐control study: the Copenhagen Stroke Study. Stroke 2000;31:2251‐6. - PubMed
Kasner 2002 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Kasner SE, Wein T, Piriyawat P, Villar‐Cordova CE, Chalela JA, Krieger DW, et al. Acetaminophen for altering body temperature in acute stroke: a randomized clinical trial. Stroke 2002;33:130‐5. - PubMed
Koennecke 2001 {published data only}
-
- Koennecke HC, Leistner S. Prophylactic antipyretic treatment with acetaminophen in acute ischemic stroke: a pilot study. Neurology 2001;57:2301‐3. - PubMed
Krieger 2001 {published data only}
-
- Krieger DW, Georgia MA, Abou‐Chebl A, Andrefsky JC, Sila CA, Katzan IL, et al. Cooling for acute ischemic brain damage (cool aid): an open pilot study of induced hypothermia in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2001;32:1847‐54. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Diringer 2004 {published data only}
-
- Diringer MN. Treatment of fever in the neurologic intensive care unit with a catheter‐based heat exchange system. Critical Care Medicine 2004;32:559‐64. - PubMed
Els 2005 {published data only}
-
- Els T, Oehm E, Voigt S, Klisch J Hetzel A, Kassubek J. Safety and therapeutical benefit of hemicraniectomy combined with mild hypothermia in comparison with hemicraniectomy alone in patients with malignant ischemic stroke. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2006;21:79‐85. - PubMed
Feng 2002 {published data only}
-
- Feng H, Shi D, Wang D, Xin X, Feng L, Zhang Y, et al. Effect of local mild hypothermia on treatment of acute intracerebral hemorrhage, a clinical study. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2002;82:1622‐4. - PubMed
Georgiadis 2002 {published data only}
-
- Georgiadis D, Schwarz S, Aschoff A, Schwab S. Hemicraniectomy and moderate hypothermia in patients with severe ischemic stroke. Stroke 2002;33:1584‐8. - PubMed
Hua 2004 {published data only}
-
- Hua T, Luo H, He XY, Li XG, Zhang ZL, Li ZX. Effects of mild hypothermia therapy on neurological function, serum superoxide dismutase and malondialdehyde in patients with acute cerebral infarction of big area. Zhongguo Linchuang Kangfu 2004;8:4504‐5.
Jian 2003 {published data only}
-
- Jian S, Yongming Q, Zhihua C, Yan C. Feasibility and safety of moderate hypothermia after acute ischemic stroke. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience 2003;21:353‐6. - PubMed
Lyden 2005 {published data only}
-
- Lyden PD, Allgren RL, Ng K, Akins P, Meyer B, Al‐Sanani F, et al. Intravascular Cooling in the Treatment of Stroke (ICTuS): early clinical experience. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases 2005;14:107‐14. - PubMed
Mayer 2001 {published data only}
-
- Mayer S, Commichau C, Scarmeas N, Presciutti M, Bates J, Copeland D. Clinical trial of an air‐circulating cooling blanket for fever control in critically ill neurologic patients. Neurology 2001;56:286‐7. - PubMed
Mayer 2004 {published data only}
-
- Mayer SA, Kowalski RG, Presciutti M, Ostapkovich ND, McGann E, Fitzsimmons BF, et al. Clinical trial of a novel surface cooling system for fever control in neurocritical care patients. Critical Care Medicine 2004;32:2508‐15. - PubMed
Meijer 2001 {published data only}
-
- Meijer RJ, Visser H, Koudstaal PJ, Dippel DWJ. Lowering body temperature in acute ischemic stroke without artificial ventilation and heavy sedation: a feasibility study. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases 2001;10:157‐60. - PubMed
Su 2004 {published data only}
-
- Su ZQ, Wang Y, Zhao QJ, Sun XY, Yang HY, Wang DS. Recent effect of local mild hypothermia for improving neurological deficits in patients with cerebral hemorrhage. Zhongguo Linchuang Kangfu 2004;8:1816‐7.
Wang 2004 {published data only}
-
- Wang H, Olivero W, Lanzino G, Elkins W, Rose J, Honings D, et al. Rapid and selective cerebral hypothermia achieved using a cooling helmet. Journal of Neurosurgery 2004;100:272‐7. - PubMed
Wang 2005 {published data only}
-
- Wang XL, Wang SM, Zhi DS, Zhang S. Mild hypothermia on patients with massive hemispheric infarction. Chinese Journal of Neurology 2005;38:255‐7.
Zhou 2003 {published data only}
-
- Zhou J, Wang J. The protective effect of subhypothermia on brain of patient with ischemic cerebrosvascular disease on different time. Zhongguo Linchuang Kangfu 2003;7:139.
References to studies awaiting assessment
Weber 2004 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Weber UJ. NOCSS: the Nordic Cooling Stroke Study. International Stroke Register Last updated on 5/25/2004.
References to ongoing studies
Guluma 2006 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
Takasato 2000 {unpublished data only}
-
- Takasato Y, Masaoka H, Wakimoto H, Naoe N, Saigusa K, Nagai M, et al. Combined local‐intraarterial thrombolysis/brain hypothermia in acute occlusion of cerebral main trunk arteries. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases 2000;9:63‐4.
Additional references
Alderson 2004
-
- Alderson P, Gadkary C, Signorini DF. Therapeutic hypothermia for head injury. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2004, Issue 4. [Art. No.: CD001048. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001048.pub2] - PubMed
Azzimondi 1998
-
- Azzimondi G, Bassein L, Nonino F, Fiorani L, Vignatelli L, Re G, et al. Fever in acute stroke worsens prognosis. A prospective study. Stroke 1998;26(11):2040‐3. - PubMed
Bernard 2002
-
- Bernard SA, Gray TW, Buist MD, Jones BM, Silvester W, Gutteridge G, et al. Treatment of comatose survivors of out‐of‐hospital cardiac arrest with induced hypothermia. New England Journal Medicine 2002;346:557‐63. - PubMed
Boysen 2001
-
- Boysen G, Christensen H. Stroke severity determines body temperature in acute stroke. Stroke 2001;32:413‐7. - PubMed
Castillo 1998
-
- Castillo J, Davalos A, Marrugat J, Noya M. Timing for fever‐related brain damage in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 1998;29(12):2455‐60. - PubMed
Chopp 1998
-
- Chopp M, Welch KM, Tidwell CD, Knight R, Helpern JA. Effect of mild hyperthermia on recovery of metabolic function after global cerebral ischemia in cats. Stroke 1998;19:1521‐5. - PubMed
Chyatte 1989
-
- Chyatte D, Elefteriades J, Kim B. Profound hypothermia and circulatory arrest for aneurysm surgery. Case report. Journal of Neurosurgery 1989;70(3):489‐91. - PubMed
Dietrich 1990
-
- Dietrich WD, Busto R, Halley M, Valdes I. The importance of brain temperature in alterations of the blood‐brain barrier following cerebral ischemia. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology 1990;49(5):486‐97. - PubMed
Dietrich 1991
-
- Dietrich WD, Halley M, Valdes I, Busto R. Interrelationships between increased vascular permeability and acute neuronal damage following temperature‐controlled brain ischemia in rats. Acta Neuropathology 1991;81(6):615‐25. - PubMed
Dirnagl 1999
-
- Dirnagl U, Iadecola C, Moskowitz MA. Pathobiology of ischaemic stroke: an integrated view. Trends in Neuroscience 1999;22:291‐7. - PubMed
Furlan 1999
-
- Furlan A, Higashida R, Wechsler L, Gent M, Rowley H, Kase C, et al. Intra‐arterial prourokinase for acute ischemic stroke. The PROACT II study: a randomized controlled trial. Prolyse in Acute Cerebral Thromboembolism. Journal of the American Medical Association 1999;282:2003‐11. - PubMed
Globus 1995
-
- Globus MY, Busto R, Lin B, Schnippering H, Ginsberg MD. Detection of free radical activity during transient global ischemia and recirculation: effects of intraischemic brain temperature modulation. Journal of Neurochemistry 1995;65(3):1250‐6. - PubMed
Henker 1998
-
- Henker RA, Brown SD, Marion DW. Comparison of brain temperature with bladder and rectal temperatures in adults with severe head injury. Neurosurgery 1998;42:1071‐5. - PubMed
Holzer 2005
-
- Holzer M, Bernard SA, Hachimi‐Idrissi S, Roine RO, Sterz F, Mullner M, et al. Hypothermia for neuroprotection after cardiac arrest: systematic review and individual patient data meta‐analysis. Critical Care Medicine 2005;33(2):414‐8. - PubMed
Huang 1999
-
- Huang ZG, Xue D, Preston E, Karbalai H, Buchan AM. Biphasic opening of the blood‐brain barrier following transient focal ischemia: effects of hypothermia. Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences 1999;26(4):298‐304. - PubMed
Jorgensen 1996
-
- Jorgensen HS, Reith J, Pedersen PM, Nakayama H, Olsen TS. Body temperature and outcome in stroke patients. Lancet 1996;348:193. - PubMed
Lopez 2006
-
- Lopez AD, Mathers CD, Ezzati M, Jamison DT, Murray CJ. Global and regional burden of disease and risk factors, 2001: systematic analysis of population health data. Lancet 2006;367:1747‐57. - PubMed
Reith 1996
-
- Reith J, Jorgensen HS, Pedersen PM, Nakayama H, Raaschou HO, Jeppesen LL, et al. Body temperature in acute stroke: relation to stroke severity, infarct size, mortality, and outcome. Lancet 1996;347(8999):422‐5. - PubMed
Rossi 2001
Saccani 1992
-
- Saccani S, Beghi C, Fragnito C, Barboso G, Fesani F. Carotid endarterectomy under hypothermic extracorporeal circulation: a method of brain protection for special patients. Journal of Cardiovascular Surgery 1992;33(3):311‐4. - PubMed
Sandercock 2008
-
- Sandercock P, Counsell C, Gubitz G, Tseng MC. Antiplatelet therapy for acute ischaemic stroke. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2008, Issue 3. [Art. No.: CD000029. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD000029.pub2] - PubMed
Schwab 1998
-
- Schwab S, Schwarz S, Spranger M, Keller E, Bertram M, Hacke W. Moderate hypothermia in the treatment of patients with severe middle cerebral artery infarction. Stroke 1998;29:2461‐6. - PubMed
Schwartz 2000
-
- Schwarz S, Hafner K, Aschoff A, Schwab S. Incidence and prognostic significance of fever following intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurology 2000;54(2):354‐61. - PubMed
Shankaran 2005
-
- Shankaran S, Laptook AR, Ehrenkranz RA, Tyson JE, McDonald SA, Donovan EF, et al. Whole‐body hypothermia for neonates with hypoxic‐ischemic encephalopathy. New England Journal of Medicine 2005;353:1574‐84. - PubMed
Van der Worp 2007a
-
- Worp HB, Sena ES, Donnan GA, Howells DW, Macleod MR. Hypothermia in animal models of acute ischaemic stroke: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Brain 2007;130:3063‐74. - PubMed
Van der Worp 2007b
-
- Worp HB, Gijn J. Clinical practice. Acute ischemic stroke. New England Journal of Medicine 2007;357:572‐9. - PubMed
Wardlaw 2003
-
- Wardlaw JM, Zoppo G, Yamaguchi T, Berge E. Thrombolysis for acute ischaemic stroke. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2003, Issue 3. [Art. No.: CD000213. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD000213] - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Correia 1999
-
- Correia M, Silva M, Veloso M. Cooling therapy for acute stroke. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 1999, Issue 4. [Art. No.: CD001247. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001247] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

