Anakinra for rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 19160248
- PMCID: PMC12296252
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005121.pub3
Anakinra for rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: In the past decade, a novel class of therapies directed against specific cytokines implicated in the disease process of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), called the 'Biologics' have greatly improved and expanded treatment for RA. Anakinra is an interleukin-1 receptor antagonist that is currently FDA-approved for moderate-severe RA that has been unresponsive to initial disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARD) therapy.
Objectives: To evaluate the clinical effectiveness and safety of anakinra in adult patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Search strategy: We searched the following electronic databases: the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (The Cochrane Library Issue 1, 2008), MEDLINE (1950 to Week 4 2008) , EMBASE (1980 to Week 5 2008), CINAHL (1982 to November 2007) and reference lists of articles.
Selection criteria: Randomized controlled trials comparing anakinra alone or in combination with DMARDs or biologics to placebo or other DMARDs or biologics in patients >18 years old with rheumatoid arthritis.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently assessed trial quality and extracted data. We contacted study authors for additional information.
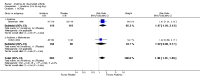
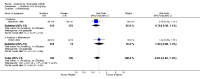
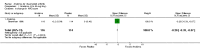
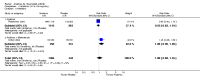
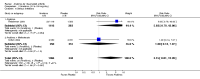
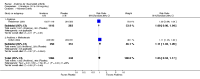
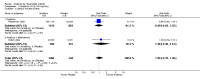
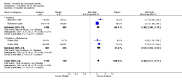
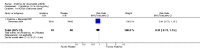
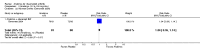
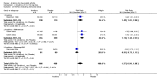
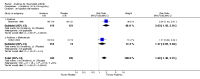
Main results: Five trials involving 2876 patients, 781 randomized to placebo and 2065 to anakinra, were included. There was a significant improvement in number of participants achieving ACR20 (38% versus 23%) who were treated with anakinra 50 to 150 mg daily versus placebo after 24 weeks. This 15% increase in patients achieving ACR20 with anakinra versus placebo is felt to be a clinically meaningful, though modest, outcome. Other efficacy data - including ACR50 (18% versus 7%), ACR70 (7% versus 2%), HAQ, visual analog score (VAS), Larsen radiographic scores, and change in erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) - all demonstrated significant improvement with anakinra 50 to 150 mg daily versus placebo as well. There were no statistically significant differences noted in most safety outcomes with treatment with anakinra versus placebo - including number of withdrawals, deaths, adverse events (total and serious), and infections (total and serious). Injection site reactions were significantly increased, occurring in 1235/1729 (71%) versus 204/729 (28%) of patients treated with anakinra versus placebo, respectively. The incidence of serious infections was clinically higher, but not statistically different, in the anakinra (25/1366 patients, 1.8%) versus placebo group (3/534 patients, 0.6%).
Authors' conclusions: Anakinra is a relatively safe and modestly efficacious biologic therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Although head to head comparison trials have not been carried out, the amount of improvement is notably less when compared to studies using other biologic therapies. More studies are needed to evaluate safety and efficacy, especially in comparison to other therapies, and adverse event data for the long-term use of Anakinra has yet to be assessed.
Conflict of interest statement
None known
Figures
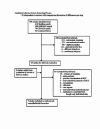























Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Bresnihan 1998 {published data only}
-
- Bresnihan B, Alvaro‐Gracia JM, Cobby M, Doherty M, Domljan Z, Emery P, et al. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with recombinant human interleukin‐1 receptor antagonist. Arthritis & Rheumatism 1998;41(12):2196‐204. - PubMed
Cohen 2002 {published data only}
-
- Cohen S, Hurd E, Cush J, Schiff M, Weinblatt ME, Moreland LW, et al. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with anakinra, a recombinant human interleukin‐1 receptor antagonist, in combination with methotrexate: results of a twenty‐four‐week, multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Arthritis & Rheumatism 2002;46(3):614‐24. - PubMed
Cohen 2004 {published data only}
-
- Cohen SB, Moreland LW, Cush JJ, Greenwald MW, Block S, Shergy WJ, et al. A multicentre, double blind, randomised, placebo controlled trial of anakinra (Kineret), a recombinant interleukin 1 receptor antagonist, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with background methotrexate. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2004;63(9):1062‐8. - PMC - PubMed
Fleischman 2003 {published data only}
-
- Fleischmann RM, Schechtman J, Bennet R, Handel ML, Burmeister GR, Tesser J, et al. Anakinra, a recombinant human interleukin‐1 receptor antagonist (r‐metHuIL‐1ra), in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A large, international, multicenter, placebo‐controlled trial. Arthritis & Rheumatism 2003;48(4):927‐34. - PubMed
Genovese 2004 {published data only}
-
- Genovese MC, Cohen S, Moreland L, Lium D, Robbins S, Newmark R, et al. Combination therapy with etanercept and anakinra in the treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis who have been treated unsuccessfully with methotrexate. Arthritis & Rheumatism 2004;50(5):1412‐9. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
AMGEN FDA 2001 {published data only}
-
- Amgen, Inc. Anakinra FDA briefing information. www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/ac/01/briefing/3779bI.htm 8/21/2001.
Bresnihan 2001 {published data only}
-
- Bresnihan B. The safety and efficacy of interleukin‐1 receptor antagonist in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Seminars in Arthritis & Rheumatism 2001;30(5 Suppl 2):17‐20. - PubMed
Bresnihan 2002 {published data only}
Bresnihan 2002b {published data only}
-
- Bresnihan B. Anakinra as a new therapeutic option in rheumatoid arthritis: clinical results and perspectives. Clinical & Experimental Rheumatology 2002;20(5 Suppl 27):S32‐4. - PubMed
Bresnihan 2004 {published data only}
-
- Bresnihan B, Newmark R, Robbins S, Genant HK, Bresnihan B, Newmark R, et al. Effects of anakinra monotherapy on joint damage in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Extension of a 24‐week randomized, placebo‐controlled trial. Arthritis & Rheumatism 2004;31(6):1103‐11. - PubMed
Burls 2004 {published data only}
-
- Burls A, Jobanputra P. The trials of anakinra. Lancet 2004;364:827‐8. - PubMed
Calabrese 2002 {published data only}
-
- Calabrese LH. Anakinra treatment of patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Annals of Pharmacotherapy 2002;36:1204‐9. - PubMed
Campion 1996 {published data only}
-
- Campion GV, Lebsack ME, Lookabaugh J, Gordon G, Catalano M. Dose‐range and dose‐frequency study of recombinant human interleukin‐1 receptor antagonist in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism 1996;39(7):1092‐101. - PubMed
Choy 2005 {published data only}
-
- Choy EHS, Smith C, Dore CJ, Scott DL. A meta‐analysis of the efficacy and toxicity of combining disease‐modifying anti‐rheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis based on patient withdrawal. Rheumatology 2005;44(11):1414‐21. - PubMed
Cohen 2003 {published data only}
-
- Cohen, S. B, J. M. Woolley, Chan W, Anakinra 960180 Study G. Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist anakinra improves functional status in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Rheumatology 2003;30(2):225‐31. - PubMed
Cohen 2004b {published data only}
-
- Cohen SB, Strand V, Aguilar D, Ofman JJ. Patient‐ versus physician‐reported outcomes in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with recombinant interleukin‐1 receptor antagonist (anakinra) therapy. Rheumatology 2004;43(6):704‐11. - PubMed
De La Mata 2007 {published data only}
-
- Mata Llord J, Crespo RG, Manzano JM. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with anakinra: A systematic review. Reumatologia Clinica 2007;3(4):153‐8. - PubMed
Dinarello 2005 {published data only}
-
- Dinarello CA. The many worlds of reducing interleukin‐1. Arthritis & Rheumatism 2005;52(7):1960‐7. - PubMed
Dougados 1992 {published data only}
-
- Dougados M, Combe B, Beveridge T, Bourdeix I, Lallemand A, Amor B, et al. IX 207‐887 in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism 1992;35(9):999‐1006. - PubMed
Drevlow 1996 {published data only}
-
- Drevlow BE, Lovis R, Haag MA, Sinacore JM, Jacobs C, Blosche C, et al. Recombinant human interleukin‐1 receptor type I in the treatment of patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism 1996;39(2):257‐65. - PubMed
Fleischmann 2002 {published data only}
-
- Fleishmann RM. Safety of anakinra, a recombinant interleukin‐1 receptor antagonist (r‐metHuIL‐1ra), in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and comparison to anti‐TNF‐alpha agents. Clinical & Experimental Rheumatology 2002;20(5 Suppl 27):S35‐41. - PubMed
Fleischmann 2006 {published data only}
Garces 2001 {published data only}
-
- Garces K. Anakinra: interleukin‐1 receptor antagonist therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Issues in Emerging Health Technologies 2001;16:1‐4. - PubMed
Garrood 2001 {published data only}
-
- Garrood T, Scott DL. Combination therapy with disease modifying anti‐rheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis. Biodrugs 2001;15(8):543‐61. - PubMed
Genant 2001 {published data only}
-
- Genant, H. K. Interleukin‐1 receptor antagonist treatment of rheumatoid arthritis patients: radiologic progression and correlation of Genant/Sharp and Larsen scoring methods. Seminars in Arthritis & Rheumatism 2001;30(5, suppl 2):26‐32. - PubMed
Haraoui 2003 {published data only}
-
- Haraoui B, Keystone EC. Anakinra, a new pharmacotherapeutic approach to treating rheumatoid arthritis. Today's Therapeutic Trends 2003;21(1):49‐59.
Jiang 2000 {published data only}
-
- Jiang Y, Genant HK, Watt I, Cobby M, Bresnihan B, Aitchison R, McCabe D. A multicenter, double‐blind, dose‐ranging, randomized, placebo‐controlled study of recombinant human interleukin‐1 receptor antagonist in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: radiologic progression and correlation of Genant and Larsen scores. Arthritis & Rheumatism 2000;43(5):1001‐9. - PubMed
Jones 2003 {published data only}
-
- Jones G, Halbert J, Crotty M, Shanahan EM, Batterham M, Ahern M. The effect of treatment on radiological progression in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review of randomized placebo‐controlled trials. Rheumatology 2003;42(1):6‐13. - PubMed
Loft 2003 {published data only}
-
- Loft AG, Tarp U, Thomsen BS, Loft AGR, Tarp U, Thomsen BS. [Anakinra in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis]. Ugeskrift for Laeger 2003;165(39):3720‐4. - PubMed
National Horizon 2001 {published data only}
-
- National Horizon Scanning Centre. Anakinra for rheumatoid arthritis ‐ horizon scanning review. Birmingham: National Horizon Scanning Centre 2001; Vol. 4.
Nixon 2007 {published data only}
-
- Nixon R, Bansback N, Brennan A. The efficacy of inhibiting tumour necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a meta‐analysis and adjusted indirect comparisons. Rheumatology 2007;46(7):1140‐7. - PubMed
Nuki 2002 {published data only}
-
- Nuki G, Bresnihan B, Bear MB, McCabe D, European Group Of Clinical I, Nuki G, et al. Long‐term safety and maintenance of clinical improvement following treatment with anakinra (recombinant human interleukin‐1 receptor antagonist) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: extension phase of a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Arthritis & Rheumatism 2002;46(11):2838‐46. - PubMed
Paget 2002 {published data only}
-
- Paget SA. Efficacy of anakinra in bone: comparison to other biologics. Advances in Therapy 2002;19(1):27‐39. - PubMed
Rau 1998 {published data only}
-
- Rau R, Sander O, Musikic P. [Treatment of chronic polyarthritis with a human recombinant interleukin 1 receptor antagonist]. Zeitschrift fur Rheumatologie 1998;57(5):312‐9. - PubMed
Rau 2003 {published data only}
Riente 2004 {published data only}
-
- Riente, L. The safety of interleukin‐1 receptor antagonist (anakinra) in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. [Italian]. Reumatismo 2004;56(1, suppl 1):74‐9. - PubMed
Schiff 2004 {published data only}
-
- Schiff MH, DiVittorio G, Tesser J, Fleischmann R, Schechtman J, Hartman S, et al. The safety of anakinra in high‐risk patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: six‐month observations of patients with comorbid conditions. Arthritis & Rheumatism 2004;50(6):1752‐60. - PubMed
Schwetz 2002 {published data only}
-
- Schwetz BA. From the Food and Drug Administration. JAMA 2002;287(1):33. - PubMed
Strand 2002 {published data only}
Strand 2004 {published data only}
-
- Strand V. Longer term benefits of treating rheumatoid arthritis: Assessment of radiographic damage and physical function in clinical trials. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 2004;22(5 Suppl 35):S57‐64. - PubMed
Tesser 2004 {published data only}
-
- Tesser J, Fleischmann R, Dore R, Bennett R, Solinger A, Joh T, Modafferi D, Schechtman J. Concomitant medication use in a large, international, multicenter, placebo controlled trial of anakinra, a recombinant interleukin 1 receptor antagonist, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Rheumatology 2004;31(4):649‐54. - PubMed
Tomoo 2005 {published data only}
-
- Tomoo T, Sumida T, et al. "[Anakinra for therapy of rheumatoid arthritis]. Nippon Rinsho ‐ Japanese Journal of Clinical Medicine 2005;63(Suppl 1):534‐7. - PubMed
Watt 2001 {published data only}
-
- Watt I, Cobby M. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis patients with interleukin‐1 receptor antagonist: radiologic assessment. Seminars in Arthritis & Rheumatism 2001;30(5 suppl 2):21‐5. - PubMed
Zundorf 2003 {published data only}
-
- Zundorf I, Dingermann T, Zundorf I, Dingermann T. [Kineret, Enbrel, Remicade and company. Recombinant drugs in rheumatoid arthritis]. Pharmazie in Unserer Zeit 2003;32(5):376‐83. - PubMed
Additional references
Abramson 2002
-
- Abramson SB, Amin A. Blocking the effects of IL‐1 in rheumatoid arthritis protects bone and cartilage. Rheumatology 2002;41:972‐80. - PubMed
ACR 2002
-
- American College of Rheumatology Subcommittee on Rheumatoid Arthritis Guidelines. Guidelines for the management of rheumatoid arthritis: 2002 update. Arthritis & Rheumatism 2002;46(2):328‐46. - PubMed
Arnett 1988
-
- Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, et al. The American Rheumatism Association revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1988;31:315‐24. - PubMed
Blumenauer 2002
Blumenauer 2003
FDA 2003 [Computer program]
-
- FDA website. Product approval information: Anakinra. www.fda.gov, 2003.
Felson 1995
-
- Felson DT, Anderson JJ, Boers M, Bombardier C, Furst D, Goldsmith C, et al. American college of rheumatology preliminary definition of improvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism 1995;38(6):727‐35. - PubMed
Felson 2007
-
- Felson, American College of Rheumatology Committee to Reevaluate Improvement Criteria. A Proposed Revision to the ACR20: The Hybrid Measure of American College of Rheumatology Response. Arthritis & Rheumatism 2007;57(2):193‐202. - PubMed
Fransen 2005
-
- Fransen J, Riel PLCM. The disease activity score and the EULAR response criteria. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 2005;23(S39):S93‐9. - PubMed
Fries 1980
-
- Fries JF, Spitz PW, Kraines RG, Holman HR. Measurement of patient outcome in arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism 1980;23:137‐45. - PubMed
Gravallese 2002
Higgins 2004
-
- Higgins JPT, Thompson SG. Controlling the risk of spurious findings from meta‐regression. Statistics in Medicine 2004;23:1663‐82. - PubMed
Kosinski 2000
-
- Kosinski M, Zhao SZ, Dedhiya S, Osterhaus JT, Ware JE. Determining minimally important changes in generic and disease‐specific health‐related quality of life questionnaires in clinical trials of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism 2000;43:1478‐87. - PubMed
Krishnan 2004
-
- Krishnan E, Sokka T, Häkkinen A, Hubert H, Hannonen P. Normative values for the Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index: benchmarking disability in the general population. Arthritis & Rheumatism 2004;50:953‐60. - PubMed
Larsen 1977
-
- Larsen A, Dale K, Eek M. Radiographic evaluation of rheumatoid arthritis and related conditions by standard reference films. Acta Radiologic Diagnosis (Stockholm) 1977;18(4):481–91. - PubMed
Lipsky 2005
-
- Lipsky RE. Rheumatoid arthritis. In: Kasper DL, Fauci AS, Longo DL, Braunwald E, Hauser SL, Jameson JL editor(s). Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine. 16. McGraw‐Hill, 2005.
Navarro‐Sarabia 2005
O'Dell 2004
-
- O'Dell JR. Rheumatoid arthritis. Current Rheumatology Diagnosis and Treatment. Imboden J, Hellman DB, Stone JH.. Vol. 1, McGraw‐Hill, 2004.
Pincus 1983
-
- Pincus T, Summey JA, Soraci SA, Jr, Wallston KA, Hummon NP. Assessment of patient satisfaction in activities of daily living using a modified Stanford Health Assessment Questionnaire. Arthritis & Rheumatism 1983;26:1346‐53. - PubMed
Prevoo 1995
-
- Prevoo MLL, Van't Hof MA, Kuper HH, Leeuwen MA, Putte LBA, Riel PLCM. Modified disease activity scores that include twenty‐eight‐joint counts. Development and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism 1995;38:44‐8. - PubMed
Prevoo 1996
-
- Prevoo MLL, Gestel AM, Van't Hof MA, Rijswijk MH, Putte LBA, Riel PLCM. Remission in a prospective study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. British Journal of Rheumatology 1996;35:1101‐5. - PubMed
Samsa 1999
-
- Samsa G, Edelman D, Rothman ML, Williams GR, Lipscomb J, Matchar D. Determining clinically important differences in health status measures: a general approach with illustration to the Health Utilities Index Mark II. Pharmacoeconomics 1999;15:141‐55. - PubMed
Sharp 1971
-
- Sharp JT, Lidsky MD, Collins LC, Moreland J. Methods of scoring the progression of radiologic changes in rheumatoid arthritis. Correlation of radiologic, clinical and laboratory abnormalities. Arthritis & Rheumatism 1971;14(6):706–20. - PubMed
Tugwell 2000
-
- Tugwell P, Wells G, Strand V, Maetzel A, Bombardier C, Crawford B, et al. Clinical improvement as reflected in measures of function and health‐related quality of life following treatment with leflunomide compared with methotrexate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: sensitivity and relative efficiency to detect a treatment effect in a twelve‐month placebo‐controlled trial. Leflunomide Rheumatoid Arthritis Investigator Group. Arthritis & Rheumatism 2000;43:506‐14. - PubMed
Tugwell 2004
-
- Tugwell P, Shea B, Boers M, Brooks P, Simon L, Strand V, et al. Evidence‐based Rheumatology. BMJ Books, 2004.
van der Heijde 1989
-
- Heijde DMFM, Riel PL, Nuver‐Zwart IH, Gribnau FW, Puttte LB. Effects of hydroxychloroquine and sulfasalazine on progression of joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 1989;1:1036‐8. - PubMed
van der Heijde 1993
-
- Heijde DM, 't Hof M, Riel PL, Putte LB. Development of a disease activity score based on judgment in clinical practice by rheumatologists. Journal of Rheumatology 1993;20(3):579‐81. - PubMed
van Gestel 1996
-
- Gestel AM, Prevoo ML, van't Hof MA, Rijswijk MH, Putte LB, Riel PL. Development and validation of the European League Against Rheumatism response criteria for rheumatoid arthritis: Comparison with the preliminary American College of Rheumatology and the World Health Organization/International League Against Rheumatism Criteria. Arthritis & Rheumatism 1996;39(1):34‐40. - PubMed
Wells 1993
-
- Wells GA, Tugwell P, Kraag GR, Baker PR, Groh J, Redelmeier DA. Minimum important difference between patients with rheumatoid arthritis: the patient's perspective. Journal of Rheumatology 1993;20:557. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

