Individual patient education for people with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 19160249
- PMCID: PMC6486318
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005268.pub2
Individual patient education for people with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Background: Type 2 diabetes is a common and costly chronic disease which is associated with significant premature mortality and morbidity. Although patient education is an integral component of diabetes care, there remain uncertainties regarding the effectiveness of different methods and modes of education.
Objectives: To evaluate the effectiveness of individual patient education on metabolic control, diabetes knowledge and psychosocial outcomes.
Search strategy: Multiple electronic bibliographic databases were searched, including The Cochrane Library, MEDLINE, Premedline, ERIC, Biosis, AMED, Psychinfo, EMBASE, CINAHL, APAIS-health, Australian Medical Index, Web of Science, dissertation abstracts and Biomed Central.
Selection criteria: Randomized controlled and controlled clinical trials which evaluated individual education for adults with type 2 diabetes. The intervention was individual face-to-face patient education while control individuals received usual care, routine treatment or group education. Only studies that assessed outcome measures at least six months from baseline were included.
Data collection and analysis: Information was extracted by two reviewers who summarized both study characteristics and outcome statistics. A meta-analysis using a fixed-effect model was performed if there were adequate studies with a specified outcome of sufficient homogeneity. For outcomes where there were too few studies or the assessment measurements were not standardized or variable, the results were summarised qualitatively.
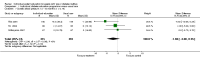
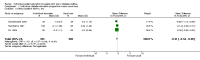
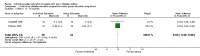
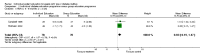
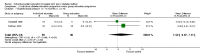
Main results: Nine studies involving 1359 participants met the inclusion criteria. Six studies compared individual education to usual care and three compared individual education to group education (361 participants). There were no long-term studies and overall the quality of the studies was not high. In the six studies comparing individual face-to-face education to usual care, individual education did not significantly improve glycaemic control (weighted mean difference (WMD) in HbA1c -0.1% (95% confidence interval (CI) -0.3 to 0.1, P = 0.33) over a 12 to 18 month period. However, there did appear to be a significant benefit of individual education on glycaemic control in a subgroup analysis of three studies involving participants with a higher mean baseline HbA1c greater than 8% (WMD -0.3% (95% CI -0.5 to -0.1, P = 0.007). In the two studies comparing individual to group education, there was no significant difference in glycaemic control between individual or group education at 12 to 18 months with a WMD in HbA1c of 0.03% (95% CI -0.02 to 0.1, P = 0.22). There was no significant difference in the impact of individual versus usual care or group education on body mass index systolic or diastolic blood pressure. There were too few studies to perform a meta-analysis on the effect of individual education on dietary self management, diabetes knowledge, psychosocial outcomes and smoking habits. No data were available on the other main outcome measures of diabetes complications or health service utilization and cost analysis in these studies.
Authors' conclusions: This systematic review suggests a benefit of individual education on glycaemic control when compared with usual care in a subgroup of those with a baseline HbA1c greater than 8%. However, overall there did not appear to be a significant difference between individual education and usual care. In the small number of studies comparing group and individual education, there was an equal impact on HbA1c at 12 to 18 months. Additional studies are needed to delineate these findings further.
Conflict of interest statement
None known
Figures





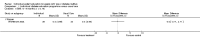







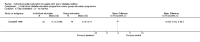
Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Campbell 1996 {published data only}
-
- Campbell E M, Redman S, Moffitt PS, Sanson‐Fisher RW. The relative effectiveness of educational and behavioral instruction programs for patients with NIDDM: a randomized trial. Diabetes Educator 1996;22(4):379‐86. - PubMed
Dalmau 2003 {published data only}
Goudswaard 2004 {published data only}
-
- Goudswaard AN, Stolk RP, Zuithoff NP, Valk HW, Rutten GE. Long‐term effects of self‐management education for patients with Type 2 diabetes taking maximal oral hypoglycaemic therapy: a randomized trial in primary care. Diabetic Medicine 2004;21(5):491‐6. - PubMed
Hawthorne 1997 {published data only}
Hiss 2001 {published data only}
-
- Hiss RG, Lou Gillard M, Armbruster BA, McClure LA. Comprehensive evaluation of community‐based diabetic patients: Effect of feedback to patients and their physicians: A randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2001;24(4):690‐4. - PubMed
Ko 2004 {published data only}
-
- Ko GTC, Li JKY, Kan ECY, Lo MKW. Effects of a structured health education programme by a diabetic education nurse on cardiovascular risk factors in Chinese Type 2 diabetic patients: a 1‐year prospective randomized study. Diabetic Medicine 2004;21:1274‐1279. - PubMed
Rickheim 2002 {published data only}
-
- Rickheim PL, Weaver TW, Flader JL, Kendall DM. Assessment of group versus individual diabetes education: a randomized study. Diabetes Care 2002;25(2):269‐74. - PubMed
Shibayama 2007 {published data only}
-
- Shibayama T, Kobayashi K, Takano A, Kadowaki T, Kazuma K. Effectiveness of lifestyle counseling by certified expert nurse of Japan for non‐insulin‐treated diabetic outpatients: A 1‐year randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice 2007;76:265‐268. - PubMed
Whittemore 2004 {published data only}
-
- Whittemore R, Melkus GD, Sullivan A, Grey M. A nurse‐coaching intervention for women with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Educator 2004;30(5):795‐804. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Aas 2005 {published data only}
-
- Aas, A M, I. Bergstad, et al. An intensified lifestyle intervention programme may be superior to insulin treatment in poorly controlled Type 2 diabetic patients on oral hypoglycaemic agents: results of a feasibility study. Diabetic Medicine 2005;22(3):316‐322. - PubMed
Anderson 2005 {published data only}
-
- Anderson, R M, M. M. Funnell, et al. Evaluating a problem‐based empowerment program for African Americans with diabetes: results of a randomized controlled trial. Ethnicity and Disease 2005;15(4):671‐8. - PubMed
Bacardi‐Gascon 2004 {published data only}
-
- Bacardi‐Gascon, M, P. Rosales‐Garay, et al. Effect of Diabetes Intervention Programs on Physical Activity among Migrant Mexican Women with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004;27(2):616. - PubMed
Baradaran 2006 {published data only}
Baran 1999 {published data only}
-
- Baran, R W, K. Crumlish, et al. Improving outcomes of community‐dwelling older patients with diabetes through pharmacist counseling. American Journal of Health‐System Pharmacy 1999;56(15):1535‐1539. - PubMed
Barcelo 2001 {published data only}
-
- Barcelo, A, S. Robles, et al. An intervention to improve diabetes control in Chile. [Spanish]. Revista Panamericana de Salud Publica/Pan American Journal of Public Health. 2001;10(5):328‐333. - PubMed
Barth 1991 {published data only}
-
- Barth, R, L. V. Campbell, et al. Intensive education improves knowledge, compliance, and foot problems in type 2 diabetes,. Diabetic Medicine. 1991;8(2):111‐117. - PubMed
Bloomgarden 1987 {published data only}
-
- Bloomgarden, Z T, W. Karmally, et al. Randomized, controlled trial of diabetic patient education: Improved knowledge without improved metabolic status,. Diabetes Care 1987;10(3):263‐272. - PubMed
Bradshaw 2006 {published data only}
-
- Bradshaw, B G. The efficacy of a resiliency training program in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Thesis Univeristy of Utah 2006.
Browning 2003 {published data only}
-
- Browning, C J, S. A. Thomas. Six‐month outcome data for the Good Life Club project: an outcomes study of diabetes self‐management.. Special Issue: The Management of Chronic Disease in Primary Care Settings 2003; Vol. 9:192‐198.
Cabrera‐Pivaral 2000 {published data only}
-
- Cabrera‐Pivaral, C E, G. Gonzalez‐Perez, et al. Effects of behavior‐modifying education in the metabolic profile of the type 2 diabetes mellitus patient. Journal of Diabetes & its Complications 2000;14(6):322‐6. - PubMed
Chen 2003 {published data only}
-
- Chen, Y S, W. C. Xu, et al. Significance of reinforcing management on limb salvage therapy in patients at high risk for diabetic foot. [Chinese],. Zhongguo Linchuang Kangfu 2003;7(18):2556‐2557.
Cleghorn 2004 {published data only}
-
- Cleghorn, G D, M. Nguyen, et al. Practice‐based interventions to improve health care for Latinos with diabetes. Ethnicity & Disease Summer 2004;1:117‐121. - PubMed
Clifford 2005 {published data only}
-
- Clifford, R M, W. A. Davis, et al. Effect of a pharmaceutical care program on vascular risk factors in type 2 diabetes: the Fremantle Diabetes Study. Diabetes Care 2005;28(4):771‐6. - PubMed
Cooper 2003 {published data only}
-
- Cooper, H, K. Booth, et al. Using combined research methods for exploring diabetes patient education. Patient Education & Counseling 2003;51(1):45‐52. - PubMed
D'Eramo‐Melkus 1992 {published data only}
-
- D'Eramo‐Melkus, G A, J. Wylie‐Rosett, et al. Metabolic impact of education in NIDDM. Diabetes Care 1992;15(7):864‐9. - PubMed
De Weerdt, I., 1991 {published data only}
-
- De Weerdt, I, A. P. Visser, et al. Randomized controlled multicentre evaluation of an education programme for insulin‐treated diabetic patients: Effects on metabolic control, quality of life, and costs of therapy,. Diabetic Medicine. 1991;8(4):338‐345. - PubMed
Deakin 2006 {published data only}
-
- Deakin, T A, J. E. Cade, et al. Structured patient education: the Diabetes X‐PERT Programme makes a difference. Diabetic Medicine 2006;23(9):944‐954. - PubMed
Di Loreto 2003 {published data only}
-
- Di Loreto, C, C. Fanelli, et al. Validation of a counseling strategy to promote the adoption and the maintenance of physical activity by type 2 diabetic subjects. Diabetes Care 2003;26(2):404‐8. - PubMed
Dijkstra 2006 {published data only}
-
- Dijkstra, R F, L. W. Niessen, et al. Patient‐centred and professional‐directed implementation strategies for diabetes guidelines: A cluster‐randomized trial‐based cost‐effectiveness analysis,. Diabetic Medicine 2006;23(2):164‐170. - PubMed
Dongbo 2003 {published data only}
Donohoe 2000 {published data only}
-
- Donohoe, E, J. A. Fletton, et al. Improving foot care for people with diabetes mellitus ‐ A randomized controlled trial of an integrated care approach,. Diabetic Medicine 2000;17(8):581‐587. - PubMed
Fan 1999 {published data only}
-
- Fan, L, J. Zhu, et al. Effect of diabetic education on patients' knowledge and self‐management ability [Chinese]. Hong Kong Nursing Journal 1999;35(2):15‐8.
Fan, M. J., G. 2002 {published data only}
-
- Fan, M J, G. H. Wu, et al. Effect evaluation of health education in 80 cases of type 2 diabetes,. Zhongguo Linchuang Kangfu 2002;6(21):3298.
Fornos 2006 {published data only}
-
- Fornos, J A, N. F. Andres, et al. A pharmacotherapy follow‐up program in patients with type‐2 diabetes in community pharmacies in Spain. Pharmacy World & Science 2006;28(2):65‐72. - PubMed
Fu 2003 {published data only}
Fukuda 1999 {published data only}
Gabbay 2006 {published data only}
-
- Gabbay, R A, I. Lendel, et al. Nurse case management improves blood pressure, emotional distress and diabetes complication screening,. Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice 2006;71(1):28‐35. - PubMed
Gaede 2001 {published data only}
-
- Gaede, P, M. Beck, et al. Limited impact of lifestyle education in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus and microalbuminuria: results from a randomized intervention study. Diabetic Medicine 2001;18(2):104‐8. - PubMed
Gallegos 2006 {published data only}
-
- Gallegos, E C, F. Ovalle‐Berumen, et al. Metabolic control of adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus through education and counseling. Journal of Nursing Scholarship 2006;38(4):344‐51. - PubMed
Gary 2003 {published data only}
-
- Gary, T L, L. R. Bone, et al. Randomized controlled trial of the effects of nurse case manager and community health worker interventions on risk factors for diabetes‐related complications in urban African Americans. Preventive Medicine 2003;37(1):23‐32. - PubMed
Gentile 2004 {published data only}
-
- Gentile, L, E. Borgo, et al. ROMEO: Rethink Organization to improve education and outcomes. A randomised controlled multicentre trial of group care for the management of type 2 diabetes. [Italian],. Giornale Italiano di Diabetologia e Metabolismo. 2004;24(1):9‐16.
Ghosh 2007 {published data only}
-
- Ghosh, H A, A. Shaar, et al. Diabetes control in 3 villages in Palestine: A community‐based quality improvement intervention,. Journal of Ambulatory Care Management. 2007;30(1):74‐78. - PubMed
Gilliland 2002 {published data only}
-
- Gilliland, S S, S. P. Azen, et al. Strong in body and spirit: Lifestyle intervention for Native American adults with diabetes in New Mexico,. Diabetes Care 2002;25(1):78‐83. - PubMed
Glasgow {published data only}
-
- Glasgow Re, T. Nutrition education and social learning interventions for type II diabetes.. Diabetes care 1989;12(2):150‐2. - PubMed
Hae 2005 {published data only}
-
- Hae, M C, S. Mitrovich, et al. Proactive case management of high‐risk patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus by a clinical pharmacist: A randomized controlled trial. American Journal of Managed Care 2005;11(4):253‐260. - PubMed
Hajdinjak 2003 {published data only}
-
- Hajdinjak, D, M. Cokolic. Improvement of control of type 2 diabetes after patient education. Diabetes & Metabolism 2003;29:(Hors serie 2).
Hanefeld 1991 {published data only}
-
- Hanefeld, M, S. Fischer, et al. Diabetes Intervention Study. Multi‐intervention trial in newly diagnosed NIDDM. 1991 Diabetes Care;14(4):308‐17. - PubMed
Holtrop 2002 {published data only}
-
- Holtrop, J S, J. Hickner, et al. "Sticking to it ‐‐ diabetes mellitus": a pilot study of an innovative behavior change program for women with type 2 diabetes. American Journal of Health Education 2002;33(3):161‐6.
Jayasuriya 2000 {published data only}
-
- Jayasuriya, R, R. Griffiths, et al. Outcome assessment of a community based model of general practitioner care diabetes patients,. Practical Diabetes International 2000;17(6):179‐182.
Jones 2003 {published data only}
-
- Jones, H, L. Edwards, et al. Changes in diabetes self‐care behaviors make a difference in glycemic control ‐ The diabetes stages of change (DiSC) study. Diabetes care 2003;26(3):732‐737. - PubMed
Jungmann 1997 {published data only}
-
- Jungmann, E, G. Jungmann, et al. Patient education of non‐insulin‐dependent diabetic patients. Effect of an ambulatory educational program on metabolism and risk factors. Fortschritte der Medizin 1997;115:20‐1. - PubMed
Kirk 2004 {published data only}
-
- Kirk, A, N. Mutrie, et al. Effects of a 12‐month activity counselling intervention on glycaemic control and on the status of cardiovascular risk factors in people with Type 2 diabetes,. Diabetologia 2004; Vol. 47, issue 5:821‐832. - PubMed
Ko, S. H., K. 2007 {published data only}
-
- Ko, S H, K. H. Song, et al. Long‐term effects of a structured intensive diabetes education programme (SIDEP) in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus ‐ A 4‐year follow‐up study,. Diabetic Medicine 2007;24(1):55‐62. - PubMed
Korhonen 1987 {published data only}
-
- Korhonen, T, M. Uusitupa, et al. Efficacy of dietary instructions in newly diagnosed non‐insulin‐dependent diabetic patients. Comparison of two different patient education regimens. Acta Medica Scandinavica 1987;222(4):323‐31. - PubMed
Kronsbein 1988 {published data only}
-
- Kronsbein, P, V. Jorgens, et al. Evaluation of a structured treatment and teaching programme on non‐insulin‐dependent diabetes. Lancet 1988;2:1407‐11. - PubMed
Kulzer 2007 {published data only}
-
- Kulzer, B, N. Hermanns, et al. Effects of self‐management training in Type 2 diabetes: a randomized, prospective trial. Diabetic Medicine 2007;24(4):415‐423. - PubMed
Laitinen 1993 {published data only}
-
- Laitinen Jh, A. Impact of intensified dietary therapy on energy and nutrient intakes and fatty acid composition of serum lipids in patients with recently diagnosed non‐insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus.. Journal of the American Dietetic Association 1993;93(3):276‐83. - PubMed
Li 2003 {published data only}
-
- Li, X. Experiences of carrying out health education in type 2 diabetes patients [Chinese]. Chinese Nursing Research 2003;17(2B):195‐7.
Li, X., Y. Cao, 2003 {published data only}
-
- Li, X, Y. Cao, et al. Effects of education on blood sugar and complications of 2 type diabetes,. Zhongguo Linchuang Kangfu 2003;7(3):509.
Litzelman 1993 {published data only}
-
- Litzelman Dk, S. Reduction of lower extremity clinical abnormalities in patients with non‐insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus. A randomized, controlled trial. Annals of internal medicine 1993;119(1):36‐41, 1993. - PubMed
Lorig 2003 {published data only}
-
- Lorig, K R, P. L. Ritter, et al. Hispanic chronic disease self‐management: a randomized community‐based outcome trial. Nursing Research 2003;52(6):361‐9. - PubMed
Lou 2006 {published data only}
-
- Lou, V W. Q, Y. Q. Zhang. Evaluating the effectiveness of a Participatory Empowerment Group for Chinese type 2 diabetes patients. Research on Social Work Practice 2006;16(5):491‐499.
Lozano 1999 {published data only}
-
- Lozano, M L, M. J. Armale, et al. [The education of type‐2 diabetics: why not in groups?].[see comment][erratum appears in Aten Primaria 1999 Jul‐Aug;24(3):178]. Atencion Primaria 1999;24(3):485‐92. - PubMed
Maislos 2004 {published data only}
-
- Maislos, M, D. Weisman. Multidisciplinary approach to patients with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus: A prospective, randomized study,. Acta Diabetologica 2004;41(2):44‐48. - PubMed
Martinus 2006 {published data only}
-
- Martinus, R, R. Corban, et al. Effect of psychological intervention on exercise adherence in type 2 diabetic subjects. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 2006;1084:350‐60. - PubMed
Mayer‐Davis 2004 {published data only}
Mazzuca 1986 {published data only}
-
- Mazzuca, S A, N. H. Moorman, et al. The Diabetes Education Study: A controlled trial of the effects of diabetes patient education,. Diabetes Care 1986;9(1):1‐10. - PubMed
Mshelia 2007 {published data only}
-
- Mshelia, D S, O. M. Akinosun, et al. Effect of increased patient‐physician contact time and health education in achieving diabetes mellitus management objectives in a resource‐poor environment. Singapore Medical Journal 2007;48(1):74‐9. - PubMed
Neder 2003 {published data only}
-
- Neder, S, P. Nadash, et al. Individualized education can improve foot care for patients with diabetes. Home Healthcare Nurse 2003;21(12):837‐40. - PubMed
Odegard 2005 {published data only}
-
- Odegard, P S, A. Goo, et al. Caring for poorly controlled diabetes mellitus: a randomized pharmacist intervention. Annals of Pharmacotherapy 2005;39(3):433‐40. - PubMed
Pedersen 2003 {published data only}
-
- Pedersen, O, P. Gaede. Intensified multifactorial intervention and cardiovascular outcome in type 2 diabetes: The Steno‐2 study,. Metabolism: Clinical & Experimental. 2003;52(8 Suppl 1):19‐23. - PubMed
Pennings‐Van 1992 {published data only}
-
- Pennings‐Van der Eerden, L, T. Ripken, et al. Evaluation of the impact of a patient education programme for NIDDM patients on knowledge, self‐care behaviour, metabolic control and lipid profiles. Gedrag & Gezondheid: Tijdschrift voor Psychologie en Gezondheid 1992;19(5):246‐260.
Philis‐Tsimikas 2004 {published data only}
-
- Philis‐Tsimikas, A, C. Walker, et al. Improvement in diabetes care of underinsured patients enrolled in Project Dulce: A community‐based, culturally appropriate, nurse case management and peer education diabetes care model. Diabetes Care 2004;27(1):110‐115. - PubMed
Pibernik‐Okanovi2004 {published data only}
-
- Pibernik‐Okanovic, M, M. Prasek, et al. Effects of an empowerment‐based psychosocial intervention on quality of life and metabolic control in type 2 diabetic patients. Patient Education and Counseling 2004;52(2):193‐9. - PubMed
Trento 2001 {published data only}
-
- Trento M, Passera P, et al. Group visits improve metabolic control in type 2 diabetes: a 2‐year follow‐up. Diabetes Care 2001;24(6):995‐1000. - PubMed
Wilson 1987 {published data only}
Wolf 2004 {published data only}
-
- Wolf, A M, M. R. Conaway, et al. Translating lifestyle intervention to practice in obese patients with type 2 diabetes: Improving Control with Activity and Nutrition (ICAN) study.[see comment]. Diabetes Care 2004;27(7):1570‐6. - PubMed
Woollard 2003 {published data only}
-
- Woollard, J, V. Burke, et al. Effects of general practice‐based nurse‐counselling on ambulatory blood pressure and antihypertensive drug prescription in patients at increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Journal of Human Hypertension 2003;17(10):689‐95. - PubMed
Additional references
AADE 2003
-
- AADE. Standards for Outcomes Measurement of Diabetes Self‐Management Education. Position Statement.. Diabetes Educator 2003;29(5):804‐16. - PubMed
ADA 1999
-
- The Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Report of the Expert Committee on the diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 1999;22 Suppl 1:S5‐19. - PubMed
ADA 2003
-
- American Diabetes Association. Economic costs of diabetes in the US in 2002.. Diabetes Care 2003;26:917‐932. - PubMed
Corabian 2001
-
- Corabian P, Harstall C. Patient Diabetes Education in the Management of Adult Type 2 Diabetes. Health Technology Assessment ‐ Alberta Heritage Foundation for Medical Research. Alberta: Alberta Heritage Foundation for Medical Research, 2001; Vol. HTA 23 Series A, issue Feb:1‐90.
Davies 2008
-
- Davies MJ, Heller S, Skinner TC, Campbell MJ, Carey ME, Cradock S, et al. Effectiveness of the diabetes education and self management for ongoing and newly diagnosed (DESMOND) programme for people with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: cluster randomised controlled trial.. BMJ 2008;336(7642):491‐5. - PMC - PubMed
Deakin 2005
Deakin 2006
-
- Deakin TA, Cade JE, Williams R, Greenwood DC. Structured patient education: the diabetes X‐PERT Programme makes a difference. Diabetic Medicine 2006;23(9):944‐54. - PubMed
Diabetes Atlas 2005
-
- International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes Atlas. www.idf.org/e‐atlas. 2005.
Eigenmann 2007
-
- Eigenmann C, Colagiuri R. Outcomes and Indicators for Diabetes Education ‐ A National Consensus Position.. Diabetes Australia 2007;June:1‐54. - PubMed
Ellis 2004
-
- Ellis SE, Speroff T, Dittus RS, Brown A, Pichert JW, Elasy TA. Diabetes patient education: a meta‐analysis and meta‐regression. Patient Education & Counseling 2004;52(1):97‐105. - PubMed
Funnell 2004
-
- Funnell MM. Patient empowerment. Critical Care Nursing Quarterly 2004;27(2):201‐4. - PubMed
Glasgow 1999
-
- Glasgow R, Fisher E, Anderson B, LeGreca A, Marrero D, Johnson S, Rubin R, Cox D. Behavioural Science in Diabetes: Contributions and Opportunities. Diabetes Care 1999;22(5):832‐43. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2005
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions 4.2.5 [updated May 2005]. In: The Cochrane Library, Issue 3, 2005. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Holmes 2003
-
- Holmes J, Gear E, Bottomley J, Gillam S, Murphy M, Williams R. Do people with type 2 diabetes and their carers lose income? (T2ARDIS‐4). Health Policy 2003;64(3):291‐6. - PubMed
Jonsson 2002
-
- Jonsson B. Revealing the cost of Type II diabetes in Europe. Diabetologia 2002;45:S5‐S12. - PubMed
King 1998
-
- King H, Aubert R, Herman W. Global Burden of diabetes, 1995‐2025 prevalence, numerical estimates and projections. Diabetes care 1998;21:1414‐1431. - PubMed
Loveman 2003
Loveman 2008
-
- Loveman E, Frampton GK, Clegg AJ. The clinical effectiveness of diabetes education models for Type 2 diabetes: a systematic review. The clinical effectiveness of diabetes education models for Type 2 diabetes: a systematic review.. Health Technol Assess Apr 2008;12(9):1‐136. - PubMed
Moher 1999
-
- Moher D, Cook DJ, Eastwood S, Olkin I, Rennie D, Stroup DF. Improving the quality of reports of meta‐analyses of randomised controlled trials: the QUOROM statement. Quality of Reporting of Meta‐analyses. Lancet 1999;354(9193):1896‐900. - PubMed
Norris 2001
-
- Norris SL, Engelgau MM, Narayan KMV. Effectiveness of self‐management training in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2001;24(3):561‐587. - PubMed
Vermeire 2003
WHO 1980
-
- WHO Expert Committee on Diabetes Mellitus. Geneva: World Health Organisation, 1980. Second report. Technical Report Series 646. - PubMed
WHO 1985
-
- WHO Expert Committee on Diabetes Mellitus. Geneva: World Health Organization, 1985. Technical Report Series 727.. - PubMed
WHO 1998
-
- Alberti KM, Zimmet PZ. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its compliactions. Part I: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabetic Medicine 1998;15:539‐53. - PubMed
Wild 2004
-
- Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global Prevalence of Diabetes: Estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care 2004;27:1047‐1053. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

