Plk1-dependent phosphorylation of FoxM1 regulates a transcriptional programme required for mitotic progression
- PMID: 19160488
- PMCID: PMC2882053
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb1767
Plk1-dependent phosphorylation of FoxM1 regulates a transcriptional programme required for mitotic progression
Abstract
Proper control of entry into and progression through mitosis is essential for normal cell proliferation and the maintenance of genome stability. The mammalian mitotic kinase Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) is involved in multiple stages of mitosis5. Here we report that Forkhead Box M1 (FoxM1), a substrate of Plk1, controls a transcriptional programme that mediates Plk1-dependent regulation of cell-cycle progression. The carboxy-terminal domain of FoxM1 binds Plk1, and phosphorylation of two key residues in this domain by Cdk1 is essential for Plk1-FoxM1 interaction. Formation of the Plk1-FoxM1 complex allows for direct phosphorylation of FoxM1 by Plk1 at G2/M and the subsequent activation of FoxM1 activity, which is required for expression of key mitotic regulators, including Plk1 itself. Thus, Plk1-dependent regulation of FoxM1 activity provides a positive-feedback loop ensuring tight regulation of transcriptional networks essential for orderly mitotic progression.
Figures
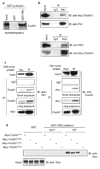
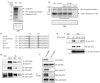
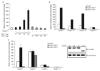

References
-
- Nigg EA. Mitotic kinases as regulators of cell division and its checkpoints. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001;2:21–32. - PubMed
-
- Norbury C, Nurse P. Animal cell cycles and their control. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1992;61:441–470. - PubMed
-
- Pines J, Rieder CL. Re-staging mitosis: a contemporary view of mitotic progression. Nature Cell Biol. 2001;3:E3–E6. - PubMed
-
- Murray AW. Recycling the cell cycle: cyclins revisited. Cell. 2004;116:221–234. - PubMed
-
- Barr FA, Sillje HH, Nigg EA. Polo-like kinases and the orchestration of cell division. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004;5:429–440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

