Pubertal hormones modulate the addition of new cells to sexually dimorphic brain regions
- PMID: 19160494
- PMCID: PMC2772186
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.2178
Pubertal hormones modulate the addition of new cells to sexually dimorphic brain regions
Abstract
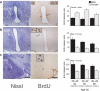
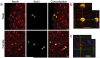
New cells, including neurons, arise in several brain regions during puberty in rats. Sex differences in pubertal addition of cells coincide with adult sexual dimorphisms: for each region, the sex that gains more cells during puberty has a larger volume in adulthood. Removing gonadal hormones before puberty eliminates these sex differences, indicating that gonadal steroids direct the addition of new cells during puberty to maintain and accentuate sexual dimorphisms in the adult brain.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

