Synaptic release of GABA by AgRP neurons is required for normal regulation of energy balance
- PMID: 19160495
- PMCID: PMC2662585
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.2167
Synaptic release of GABA by AgRP neurons is required for normal regulation of energy balance
Abstract
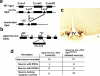
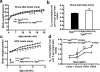
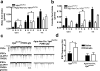
The physiologic importance of GABAergic neurotransmission in hypothalamic neurocircuits is unknown. To examine the importance of GABA release from agouti-related protein (AgRP) neurons (which also release AgRP and neuropeptide Y), we generated mice with an AgRP neuron-specific deletion of vesicular GABA transporter. These mice are lean, resistant to obesity and have an attenuated hyperphagic response to ghrelin. Thus, GABA release from AgRP neurons is important in regulating energy balance.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

