Arterial spin labeling perfusion MRI in pediatric arterial ischemic stroke: initial experiences
- PMID: 19161176
- PMCID: PMC2728589
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.21641
Arterial spin labeling perfusion MRI in pediatric arterial ischemic stroke: initial experiences
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the feasibility and utility of arterial spin labeling (ASL) perfusion MRI for characterizing alterations of cerebral blood flow (CBF) in pediatric patients with arterial ischemic stroke (AIS).
Materials and methods: Ten children with AIS were studied within 4 to 125 hours following symptom onset, using a pulsed ASL (PASL) protocol attached to clinically indicated MR examinations. The interhemisphere perfusion deficit (IHPD) was measured in predetermined vascular territories and infarct regions of restricted diffusion, which were compared with the degree of arterial stenosis and volumes of ischemic infarcts.
Results: Interpretable CBF maps were obtained in all 10 patients, showing simple lesion in nine patients (five hypoperfusion, two hyperperfusion, and two normal perfusion) and complex lesions in one patient. Both acute and follow-up infarct volumes were significantly larger in cases with hypoperfusion than in either hyper- or normal perfusion cases. The IHPD was found to correlate with the degree of stenosis, diffusion lesion, and follow-up T(2) infarct volumes. Mismatch between perfusion and diffusion lesions was observed. Brain regions presenting delayed arterial transit effects were tentatively associated with positive outcome.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates the clinical utility of ASL in the neuroimaging diagnosis of pediatric AIS.
Figures

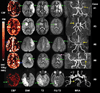
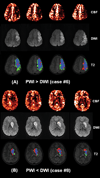


References
-
- Fullerton HJ, Chetkovich DM, Wu YW, Smith WS, Johnston SC. Deaths from stroke in US children, 1979 to 1998. Neurology. 2002;59:34–39. - PubMed
-
- Ganesan V, Prengler M, McShane MA, Wade AM, Kirkham FJ. Investigation of risk factors in children with arterial ischemic stroke. Ann Neurol. 2003;53:167–173. - PubMed
-
- Fullerton HJ, Wu YW, Zhao S, Johnston SC. Risk of stroke in children: ethnic and gender disparities. Neurology. 2003;61:189–194. - PubMed
-
- Lynch JK, Hirtz DG, DeVeber G, Nelson KB. Report of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke workshop on perinatal and childhood stroke. Pediatrics. 2002;109:116–123. - PubMed
-
- Braun KP, Rafay MF, Uiterwaal CS, Pontigon AM, DeVeber G. Mode of onset predicts etiological diagnosis of arterial ischemic stroke in children. Stroke. 2007;38:298–302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

