Metabolic alterations: a biomarker for radiation-induced normal brain injury-an MR spectroscopy study
- PMID: 19161192
- PMCID: PMC2679518
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.21657
Metabolic alterations: a biomarker for radiation-induced normal brain injury-an MR spectroscopy study
Abstract
Purpose: To assess if interval changes in metabolic status in normal cerebral tissue after radiation therapy (RT) can be detected by 2D CSI (chemical shift imaging) proton spectroscopy.
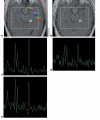
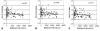
Materials and methods: Eleven patients with primary brain tumors undergoing cranial radiation therapy (RT) were included. 2D-CSI MRS was performed before, during, and after the course of RT with the following parameters: TE/TR 144/1500 ms, field of view (FOV) 24, thickness 10 mm, matrix 16 x 16. The metabolic ratios choline/creatine (Cho/Cr), N-acetylaspartate (NAA)/Cr, and NAA/Cho in normal brain tissue were calculated.
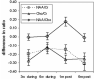
Results: NAA/Cr and Cho/Cr were significantly decreased at week 3 during RT and at 1 month and 6 months after RT compared to values prior to RT (P < 0.01). The NAA/Cr ratio decreased by -0.19 +/- 0.05 (mean +/- standard error [SE]) at week 3 of RT, -0.14 +/- 0.06 at the last week of RT, -0.14 +/- 0.05 at 1 month after RT, and -0.30 +/- 0.08 at 6 months after RT compared to the pre-RT value of 1.43 +/- 0.04. The Cho/Cr ratio decreased by -0.27 +/- 0.05 at week 3 of RT, -0.11 +/- 0.05 at the last week of RT, -0.26 +/- 0.05 at 1 month after RT and -0.25 +/- 0.07 at 6 months after RT from the pre-RT value of 1.29 +/- 0.03. Changes in Cho/Cr were correlated with the interaction of the radiation dose and dose-volume at week 3 of RT, during the last week of RT (P < 0.005), and at 1 month after RT (P = 0.017).
Conclusion: The results of this study suggest that MRS can detect early metabolic changes in normal irradiated brain tissue.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transient metabolic changes observed with proton MR spectroscopy in normal human brain after radiation therapy.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1998 Jan 15;40(2):279-86. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(97)00714-1. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1998. PMID: 9457810
-
MR spectroscopy using normalized and non-normalized metabolite ratios for differentiating recurrent brain tumor from radiation injury.Acad Radiol. 2011 Sep;18(9):1101-8. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2011.05.006. Acad Radiol. 2011. PMID: 21820634
-
Differentiation between brain tumor recurrence and radiation injury using MR spectroscopy.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005 Dec;185(6):1471-6. doi: 10.2214/AJR.04.0933. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005. PMID: 16304000
-
Multivoxel 3D proton MR spectroscopy in the distinction of recurrent glioma from radiation injury.J Neurooncol. 2007 Aug;84(1):63-9. doi: 10.1007/s11060-007-9341-3. Epub 2007 Feb 14. J Neurooncol. 2007. PMID: 17619225 Clinical Trial.
-
Distinction between recurrent glioma and radiation injury using magnetic resonance spectroscopy in combination with diffusion-weighted imaging.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007 May 1;68(1):151-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.12.001. Epub 2007 Feb 7. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007. PMID: 17289287
Cited by
-
Advances in Magnetic Resonance and Positron Emission Tomography Imaging: Assessing Response in the Treatment of Low-Grade Glioma.Semin Radiat Oncol. 2015 Jul;25(3):172-80. doi: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2015.02.003. Epub 2015 Feb 21. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26050587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain diffusion MRI biomarkers after oncology treatments.Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2024 Feb 16;28(6):823-834. doi: 10.5603/rpor.98728. eCollection 2023. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2024. PMID: 38515826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Compatibility between 3T 1H SV-MRS data and automatic brain tumour diagnosis support systems based on databases of 1.5T 1H SV-MRS spectra.MAGMA. 2011 Feb;24(1):35-42. doi: 10.1007/s10334-010-0241-8. Epub 2011 Jan 20. MAGMA. 2011. PMID: 21249420
-
Delayed effects of radiation in adipose tissue reflect progenitor damage and not cellular senescence.Geroscience. 2023 Feb;45(1):507-521. doi: 10.1007/s11357-022-00660-x. Epub 2022 Sep 22. Geroscience. 2023. PMID: 36136223 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging changes following stereotactic radiosurgery for metastatic intracranial tumors: differentiating pseudoprogression from tumor progression and its effect on clinical practice.Neurosurg Rev. 2014 Apr;37(2):193-201; discussion 201. doi: 10.1007/s10143-013-0504-8. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Neurosurg Rev. 2014. PMID: 24233257 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer Statstics 2008. CA A Cancer Journal for Clin. 2008;58:71–96. - PubMed
-
- Legler JM, Ries LA Gloeckler, Smith MA, et al. Brain and other central nervous system cancers: recent trends in incidence and mortality. J of the National Cancer Institute. 1998;91:1382–90. - PubMed
-
- Schultheiss TE, Kun LE, Ang KK, et al. Radiation response of the central nervous system. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995;31:1093–112. - PubMed
-
- Tofilon PJ, Fike JR. The radioresponse of the central nervous system: a dynamic process. Radiat Res. 2000;153:357–70. PubMed. - PubMed
-
- Constine LS, Konski A, Ekholm S, et al. Adverse effects of brain irradiation correlated with MR and CT imaging. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1988;15:319–30. - PubMed

