Pseudo cardiac tamponade in the setting of excess pericardial fat
- PMID: 19161596
- PMCID: PMC2632988
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-7120-7-3
Pseudo cardiac tamponade in the setting of excess pericardial fat
Abstract
Cardiac tamponade is the phenomenon of hemodynamic compromise caused by a pericardial effusion. Following a myocardial infarction, the most common causes of pericardial fluid include early pericarditis, Dressler's syndrome, and hemopericardium secondary to a free wall rupture. On transthoracic echocardiography, pericardial fluid appears as an echo-free space in between the visceral and parietal layers of the pericardium. Pericardial fat has a similar appearance on echocardiography and it may be difficult to discern the two entities. We present a case of a post-MI patient demonstrating pseudo tamponade physiology in the setting of excessive pericardial fat.
Figures
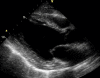
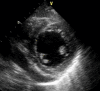

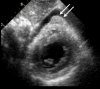

References
-
- Feigenbaum's Echocardiography 6th ed. Chapter 9 pericardial diseases. 2007.
-
- Rosito GA, Massaro JM, Hoffmann U, Ruberg FL, Mahabadi AA, Vasan RS, O'Donnell CJ, Fox CS. Pericardial fat, visceral abdominal fat, cardiovascular disease risk factors, and vascular calcification in a community-based sample: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 2008;117:605–13. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.743062. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

