Gender, race/ethnicity, personality, and interleukin-6 in urban primary care patients
- PMID: 19162168
- PMCID: PMC2694851
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2008.12.009
Gender, race/ethnicity, personality, and interleukin-6 in urban primary care patients
Abstract
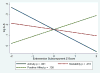
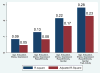
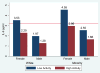
Gender, race/ethnicity, and personality are markers of significant psychosocial and biological variability. Each may have implications for allostatic load and resulting inflammatory processes, yet findings have been largely mixed. We investigated whether women, minorities, and those higher in Neuroticism and lower in Extraversion were at risk for elevated circulating levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin (IL)-6 in a sample of 103 middle aged and older urban primary care patients. Regression analyses controlling for age, education, current depression levels, and chronic medical conditions revealed that women, minorities, and individuals lower in Extraversion had higher circulating levels of IL-6. Analyses of more specific personality traits revealed that the sociability and positive emotions components of Extraversion were unassociated with IL-6, but the activity facet-reflecting dispositional vigor and energy-was robustly associated with IL-6. The difference between high (+1 Standard Deviation (SD)) and low (-1 SD) trait activity was sufficient to shift IL-6 levels beyond a previously established high risk cut-point in both white and minority women. These findings suggest that while broad group differences between genders and races/ethnicities exist, personality represents an important source of individual differences in inflammation within groups. Future work should examine to what extent IL-6 levels are linked to temperament or genetic activity levels vs. physical activity itself, and whether IL-6 levels may be reduced by boosting regular activity levels in demographic segments such as women and minorities who appear susceptible to greater inflammation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Racial and Ethnic Digital Divides in Posting COVID-19 Content on Social Media Among US Adults: Secondary Survey Analysis.J Med Internet Res. 2020 Jul 3;22(7):e20472. doi: 10.2196/20472. J Med Internet Res. 2020. PMID: 32568726 Free PMC article.
-
High neuroticism and low conscientiousness are associated with interleukin-6.Psychol Med. 2010 Sep;40(9):1485-93. doi: 10.1017/S0033291709992029. Epub 2009 Dec 9. Psychol Med. 2010. PMID: 19995479 Free PMC article.
-
Big 5 personality traits and interleukin-6: evidence for "healthy Neuroticism" in a US population sample.Brain Behav Immun. 2013 Feb;28:83-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2012.10.020. Epub 2012 Oct 31. Brain Behav Immun. 2013. PMID: 23123863 Free PMC article.
-
Dispositional depression and hostility are associated with inflammatory markers of cardiovascular disease in African Americans.Brain Behav Immun. 2013 Feb;28:72-82. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2012.10.019. Epub 2012 Oct 30. Brain Behav Immun. 2013. PMID: 23123367
-
Peripheral levels of C-reactive protein, tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6, and interleukin-1β across the mood spectrum in bipolar disorder: A meta-analysis of mean differences and variability.Brain Behav Immun. 2021 Oct;97:193-203. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2021.07.014. Epub 2021 Jul 28. Brain Behav Immun. 2021. PMID: 34332041
Cited by
-
The inflammatory immune system after wake up in healthy male individuals: A highly standardized and controlled study.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2022 Aug 28;25:100504. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2022.100504. eCollection 2022 Nov. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2022. PMID: 36093437 Free PMC article.
-
IL-6 after wake-up in human males: Exposure to red versus blue light and the interplay with cortisol.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2024 Aug 2;40:100833. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2024.100833. eCollection 2024 Oct. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2024. PMID: 39252985 Free PMC article.
-
Personality is of central concern to understand health: towards a theoretical model for health psychology.Health Psychol Rev. 2013 May;7(Suppl 1):S32-S70. doi: 10.1080/17437199.2010.547985. Epub 2013 May 28. Health Psychol Rev. 2013. PMID: 23772230 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin 6 and Development of Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction in the General Population.J Am Heart Assoc. 2021 Jun;10(11):e018549. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.018549. Epub 2021 May 17. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021. PMID: 33998283 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in stress-induced alcohol intake: a review of preclinical studies focused on amygdala and inflammatory pathways.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022 Jul;239(7):2041-2061. doi: 10.1007/s00213-022-06120-w. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022. PMID: 35359158 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allison MA, Criqui MH, McClelland RL, Scot J, McDermott K, Liu A, Folsom A, Bertoni A, Sharrett A, Homma S. The effect of novel cardiovascular risk factors on ethnic-specific odds for peripheral arterial disease in the Multi-ethnict Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2006;48(6):1190–1197. - PubMed
-
- Bergson H. In: Creative evolution. Mitchell Arthur., translator. New York: Henry Holt and Company; 1911.
-
- Berkman LF, Glass T. Social integration, social networks, social support, and health. In: Berkman LF, Kawachi I, editors. Social epidemiology. New York: Oxford University Press; 2000. pp. 137–173.
-
- Berkman LF, Kawachi I, editors. Social epidemiology. New York: Oxford University Press; 2000.
-
- Bouhuys AL, Flentge F, Oldehinkel AJ, van den Berg Marjan D. Potential psychosocial mechanisms linking depression to immune function in elderly subjects. Psychiatry Research. 2004;127(3):237–245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

