N-cadherin modulates voltage activated calcium influx via RhoA, p120-catenin, and myosin-actin interaction
- PMID: 19162191
- PMCID: PMC2883866
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcn.2008.12.007
N-cadherin modulates voltage activated calcium influx via RhoA, p120-catenin, and myosin-actin interaction
Abstract
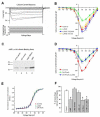
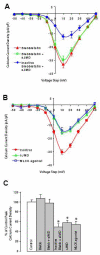
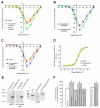
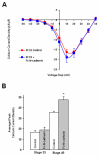
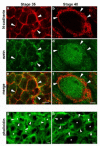
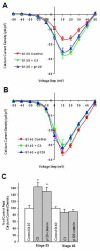
N-cadherin is a transmembrane adhesion receptor that contributes to neuronal development and synapse formation through homophilic interactions that provide structural-adhesive support to contacts between cell membranes. In addition, N-cadherin homotypic binding may initiate cell signaling that regulates neuronal physiology. In this study, we investigated signaling capabilities of N-cadherin that control voltage activated calcium influx. Using whole-cell voltage clamp recording of isolated inward calcium currents in freshly isolated chick ciliary ganglion neurons we show that the juxtamembrane region of N-cadherin cytoplasmic domain regulates high-threshold voltage activated calcium currents by interacting with p120-catenin and activating RhoA. This regulatory mechanism requires myosin interaction with actin. Furthermore, N-cadherin homophilic binding enhanced voltage activated calcium current amplitude in dissociated neurons that have already developed mature synaptic contacts in vivo. The increase in calcium current amplitude was not affected by brefeldin A suggesting that the effect is caused via direct channel modulation and not by increasing channel expression. In contrast, homotypic N-cadherin interaction failed to regulate calcium influx in freshly isolated immature neurons. However, RhoA inhibitors enhanced calcium current amplitude in these immature neurons, suggesting that the inhibitory effect of RhoA on calcium entry is regulated during neuronal development and synapse maturation. These results indicate that N-cadherin modulates voltage activated calcium entry by a mechanism that involves RhoA activity and its downstream effects on the cytoskeleton, and suggest that N-cadherin provides support for synaptic maturation and sustained synaptic activity by facilitating voltage activated calcium influx.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assembly of the N-cadherin complex during synapse formation involves uncoupling of p120-catenin and association with presenilin 1.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2005 Sep;30(1):118-30. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2005.06.005. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2005. Corrected and republished in: Mol Cell Neurosci. 2005 Dec;30(4):611-23. PMID: 16046145 Corrected and republished.
-
Binding site for p120/delta-catenin is not required for Drosophila E-cadherin function in vivo.J Cell Biol. 2003 Feb 3;160(3):313-9. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200207160. Epub 2003 Jan 27. J Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12551956 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of RhoA by p120 catenin.Nat Cell Biol. 2000 Sep;2(9):637-44. doi: 10.1038/35023588. Nat Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10980705
-
Emerging roles for p120-catenin in cell adhesion and cancer.Oncogene. 2004 Oct 18;23(48):7947-56. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208161. Oncogene. 2004. PMID: 15489912 Review.
-
N-cadherin signaling in synapse formation and neuronal physiology.Mol Neurobiol. 2006 Jun;33(3):237-52. doi: 10.1385/MN:33:3:237. Mol Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 16954598 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Gene-Set Analysis Identifies Molecular Mechanisms Associated with ALS.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 16;24(4):4021. doi: 10.3390/ijms24044021. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835433 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine monophosphate-activated kinase alpha1 promotes endothelial barrier repair.FASEB J. 2011 Oct;25(10):3356-65. doi: 10.1096/fj.10-179218. Epub 2011 Jun 16. FASEB J. 2011. PMID: 21680893 Free PMC article.
-
Glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor attenuates neuropathic pain in a mouse model of chronic constriction injury: possible involvement of E-cadherin/p120ctn signaling.J Mol Neurosci. 2014;54(2):156-63. doi: 10.1007/s12031-014-0266-y. Epub 2014 Mar 6. J Mol Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24599758
-
Synchronous and asynchronous transmitter release at nicotinic synapses are differentially regulated by postsynaptic PSD-95 proteins.J Neurosci. 2009 Dec 16;29(50):15770-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4951-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 20016093 Free PMC article.
-
MT5-MMP, ADAM-10, and N-cadherin act in concert to facilitate synapse reorganization after traumatic brain injury.J Neurotrauma. 2012 Jul 1;29(10):1922-40. doi: 10.1089/neu.2012.2383. Epub 2012 May 14. J Neurotrauma. 2012. PMID: 22489706 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anastasiadis PZ, Reynolds AB. The p120 catenin family: complex roles in adhesion, signaling and cancer. J Cell Sci. 2000;113(Pt 8):1319–1334. - PubMed
-
- Anastasiadis PZ, Moon SY, Thoreson MA, Mariner DJ, Crawford HC, Zheng Y, Reynolds AB. Inhibition of RhoA by p120 catenin. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2:637–644. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

