A comparison of automated segmentation and manual tracing for quantifying hippocampal and amygdala volumes
- PMID: 19162198
- PMCID: PMC2714773
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.12.033
A comparison of automated segmentation and manual tracing for quantifying hippocampal and amygdala volumes
Abstract
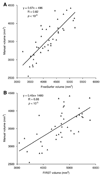
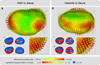
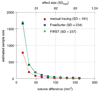
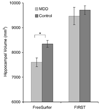
Large databases of high-resolution structural MR images are being assembled to quantitatively examine the relationships between brain anatomy, disease progression, treatment regimens, and genetic influences upon brain structure. Quantifying brain structures in such large databases cannot be practically accomplished by expert neuroanatomists using hand-tracing. Rather, this research will depend upon automated methods that reliably and accurately segment and quantify dozens of brain regions. At present, there is little guidance available to help clinical research groups in choosing such tools. Thus, our goal was to compare the performance of two popular and fully automated tools, FSL/FIRST and FreeSurfer, to expert hand tracing in the measurement of the hippocampus and amygdala. Volumes derived from each automated measurement were compared to hand tracing for percent volume overlap, percent volume difference, across-sample correlation, and 3-D group-level shape analysis. In addition, sample size estimates for conducting between-group studies were computed for a range of effect sizes. Compared to hand tracing, hippocampal measurements with FreeSurfer exhibited greater volume overlap, smaller volume difference, and higher correlation than FIRST, and sample size estimates with FreeSurfer were closer to hand tracing. Amygdala measurement with FreeSurfer was also more highly correlated to hand tracing than FIRST, but exhibited a greater volume difference than FIRST. Both techniques had comparable volume overlap and similar sample size estimates. Compared to hand tracing, a 3-D shape analysis of the hippocampus showed FreeSurfer was more accurate than FIRST, particularly in the head and tail. However, FIRST more accurately represented the amygdala shape than FreeSurfer, which inflated its anterior and posterior surfaces.
Figures









Comment in
-
Improving the reliability of manual and automated methods for hippocampal and amygdala volume measurements.Neuroimage. 2009 Nov 15;48(3):497-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.05.004. Epub 2009 May 13. Neuroimage. 2009. PMID: 19442748 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Apostolova LG, Dinov ID, Dutton RA, Hayashi KM, Toga AW, Cummings JL, Thompson PM. 3D comparison of hippocampal atrophy in amnestic mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease [Erratum appears in Brain. 2007 Sep;130(Pt 9):2474] Brain. 2006;129:2867–2873. - PubMed
-
- Barnes J, Foster J, Boyes RG, Pepple T, Moore EK, Schott JM, et al. A comparison of methods for the automated calculation of volumes and atrophy rates in the hippocampus. NeuroImage. 2008;40:1655–1671. - PubMed
-
- Campbell S, Marriott M, Nahmias C, MacQueen GM. Lower hippocampal volume in patients suffering from depression: a meta-analysis. Am. J. Psychiatry. 2004;161:598–607. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

