Combining multiple microarray studies using bootstrap meta-analysis
- PMID: 19164001
- PMCID: PMC5003036
- DOI: 10.1109/IEMBS.2008.4650498
Combining multiple microarray studies using bootstrap meta-analysis
Abstract
Microarray technology has enabled us to simultaneously measure the expression of thousands of genes. Using this high-throughput data collection, we can examine subtle genetic changes between biological samples and build predictive models for clinical applications. Although microarrays have dramatically increased the rate of data collection, sample size is still a major issue in feature selection. Previous methods show that microarray data combination is successful in improving selection when using z-scores and fold change. We propose a wrapper based gene selection technique that combines bootstrap estimated classification errors for individual genes across multiple datasets. The bootstrap is an unbiased estimator of classification error and has been shown to be effective for small sample data. Coupled with data combination across multiple data sets, we show that this meta-analytic approach improves gene selection.
Figures
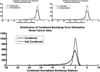
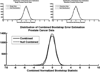
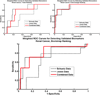
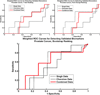
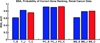
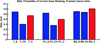


Similar articles
-
Handling gene redundancy in microarray data using Grey Relational Analysis.Int J Data Min Bioinform. 2008;2(2):134-44. doi: 10.1504/ijdmb.2008.019094. Int J Data Min Bioinform. 2008. PMID: 18767351
-
What should be expected from feature selection in small-sample settings.Bioinformatics. 2006 Oct 1;22(19):2430-6. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl407. Epub 2006 Jul 26. Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 16870934
-
Knowledge guided analysis of microarray data.J Biomed Inform. 2006 Aug;39(4):401-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2005.08.004. Epub 2005 Sep 15. J Biomed Inform. 2006. PMID: 16214421
-
Classification based upon gene expression data: bias and precision of error rates.Bioinformatics. 2007 Jun 1;23(11):1363-70. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm117. Epub 2007 Mar 28. Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 17392326 Review.
-
Filter versus wrapper gene selection approaches in DNA microarray domains.Artif Intell Med. 2004 Jun;31(2):91-103. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2004.01.007. Artif Intell Med. 2004. PMID: 15219288 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated Left Ventricular Global Transcriptome and Proteome Profiling in Human End-Stage Dilated Cardiomyopathy.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 6;11(10):e0162669. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162669. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27711126 Free PMC article.
-
Left ventricular global transcriptional profiling in human end-stage dilated cardiomyopathy.Genomics. 2009 Jul;94(1):20-31. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2009.03.003. Epub 2009 Mar 28. Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19332114 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Irizarry RA, et al. Multiple-laboratory comparison of microarray platforms. Nature Methods. 2005;2(5):345–350. - PubMed
-
- Patterson T, et al. Performance comparison of one-color and two-color platforms within the MicroArray Quality Control (MAQC) project. Nature Biotechnology. 2006;24(9):1140–1150. - PubMed
-
- Vo TM, et al. Reproducibility of Differential Gene Detection Across Multiple Microarray Studies; Proc. 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBS; 2007. - PubMed
-
- Troyanskaya O, et al. Nonparametric methods for identifying differentially expressed genes in microarray data. Bioinformatics. 2002;18(11):1454–1461. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
