Mapping and identification of GABAergic neurons in transgenic mice projecting to cardiac vagal neurons in the nucleus ambiguus using photo-uncaging
- PMID: 19164103
- PMCID: PMC2695650
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.91134.2008
Mapping and identification of GABAergic neurons in transgenic mice projecting to cardiac vagal neurons in the nucleus ambiguus using photo-uncaging
Abstract
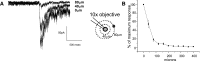
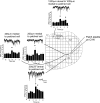
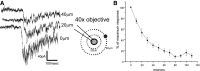
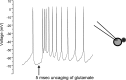
The neural control of heart rate is determined primarily by the activity of preganglionic parasympathetic cardiac vagal neurons (CVNs) originating in the nucleus ambiguus (NA) in the brain stem. GABAergic inputs to CVNs play an essential role in determining the activity of these neurons including a robust inhibition during each inspiratory burst. The origin of GABAergic innervation has yet to be determined however. A transgenic mouse line expressing green florescent protein (GFP) in GABAergic cells was used in conjunction with caged glutamate to identify both clusters and individual GABAergic neurons that evoke inhibitory GABAergic synaptic responses in CVNs. Transverse slices were taken with CVNs patch-clamped in the whole cell configuration. Sections containing both the pre-Botzinger complex as well as the calamus scriptorius were divided into approximately 90 quadrants, each 200 x 200 microm and were sequentially photostimulated. Inhibitory post synaptic currents (IPSCs) were recorded in CVNs after a 5-ms photostimulation of 50 microM caged glutamate. The four areas that contained GABAergic cells projecting to CVNs were 200 microm medial, 400 microm medial, 200 microm ventral, and 1,200 microm dorsal and 1,000 microm medial to patched CVNs. Once foci of GABAergic cells projecting to CVNs were determined, photostimulation of individual GABAergic neurons was conducted. The results from this study suggest that GABAergic cells located in four specific areas project to CVNs, and that these cells can be individually identified and stimulated using photouncaging to recruit GABAergic neurotransmission to CVNs.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synaptic activation of cardiac vagal neurons by capsaicin sensitive and insensitive sensory neurons.Brain Res. 2003 Jul 25;979(1-2):210-5. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(03)02937-8. Brain Res. 2003. PMID: 12850588
-
The lateral paragigantocellular nucleus modulates parasympathetic cardiac neurons: a mechanism for rapid eye movement sleep-dependent changes in heart rate.J Neurophysiol. 2010 Aug;104(2):685-94. doi: 10.1152/jn.00228.2010. Epub 2010 May 19. J Neurophysiol. 2010. PMID: 20484535 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of D2-like dopamine receptors inhibits GABA and glycinergic neurotransmission to pre-motor cardiac vagal neurons in the nucleus ambiguus.Neuroscience. 2013 Sep 5;247:213-26. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.05.039. Epub 2013 May 29. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 23727508 Free PMC article.
-
α1-adrenergic receptors facilitate inhibitory neurotransmission to cardiac vagal neurons in the nucleus ambiguus.Neuroscience. 2011 Oct 13;193:154-61. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.07.024. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Neuroscience. 2011. PMID: 21771639 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic and neurotransmitter activation of cardiac vagal neurons in the nucleus ambiguus.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001 Jun;940:237-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb03680.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001. PMID: 11458681 Review.
Cited by
-
Clonidine, an alpha2-receptor agonist, diminishes GABAergic neurotransmission to cardiac vagal neurons in the nucleus ambiguus.Brain Res. 2010 Aug 6;1347:65-70. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.06.001. Epub 2010 Jun 8. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 20553874 Free PMC article.
-
Sudden unexpected death in Dravet syndrome: respiratory and other physiological dysfunctions.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2013 Nov 1;189(2):324-8. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2013.06.026. Epub 2013 Jul 9. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23850567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of Brainstem Pro-opiomelanocortin Neurons Produces Opioidergic Analgesia, Bradycardia and Bradypnoea.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 14;11(4):e0153187. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153187. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27077912 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac vagal motor neurons.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2025 Aug;93:103068. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2025.103068. Epub 2025 Jun 25. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40570503 Review.
-
Central and Peripheral GABA(A) Receptor Regulation of the Heart Rate Depends on the Conscious State of the Animal.Adv Pharmacol Sci. 2011;2011:578273. doi: 10.1155/2011/578273. Epub 2011 Nov 17. Adv Pharmacol Sci. 2011. PMID: 22162673 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Babic T, de Oliveira CV, Ciriello J. Collateral axonal projections from rostral ventromedial medullary nitric oxide synthase containing neurons to brainstem autonomic sites. Brain Res 1211: 44–56, 2008. - PubMed
-
- Batten TF Immunolocalization of putative neurotransmitters innervating autonomic regulating neurons (correction of neurons) of cat ventral medulla. Brain Res Bull 37: 487–506, 1995. - PubMed
-
- Braccialli AL, Bonagamba LG, Machado BH. Glutamatergic and purinergic mechanisms on respiratory modulation in the caudal NTS of awake rats. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 161: 246–252, 2008. - PubMed
-
- Bouairi E, Kamendi H, Wang X, Gorini C, Mendelowitz D. Multiple types of GABAA receptors mediate inhibition in brain stem parasympathetic cardiac neurons in the nucleus ambiguus. J Neurophysiol 96: 3266–3272, 2006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

