A critical role for IL-21 receptor signaling in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus in BXSB-Yaa mice
- PMID: 19164519
- PMCID: PMC2635818
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0807309106
A critical role for IL-21 receptor signaling in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus in BXSB-Yaa mice
Abstract
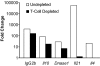
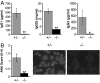
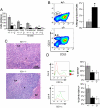
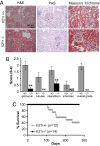
Interleukin 21 (IL-21) is a pleiotropic cytokine produced by CD4 T cells that affects the differentiation and function of T, B, and NK cells by binding to a receptor consisting of the common cytokine receptor gamma chain and the IL-21 receptor (IL-21R). IL-21, a product associated with IL-17-producing CD4 T cells (T(H)17) and follicular CD4 T helper cells (T(FH)), has been implicated in autoimmune disorders including the severe systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)-like disease characteristic of BXSB-Yaa mice. To determine whether IL-21 plays a significant role in this disease, we compared IL-21R-deficient and -competent BXSB-Yaa mice for multiple parameters of SLE. The deficient mice showed none of the abnormalities characteristic of SLE in IL-21R-competent Yaa mice, including hypergammaglobulinemia, autoantibody production, reduced frequencies of marginal zone B cells and monocytosis, renal disease, and premature morbidity. IL-21 production associated with this autoimmune disease was not a product of T(H)17 cells and was not limited to conventional CXCR5(+) T(FH) but instead was produced broadly by ICOS(+) CD4(+) splenic T cells. IL-21 arising from an abnormal population of CD4 T cells is thus central to the development of this lethal disease, and, more generally, could play an important role in human SLE and related autoimmune disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors are listed as co-inventors on applications for and/or issued patents related to IL-21.
Figures
References
-
- Murphy ED, Roths JB. A Y chromosome associated factor in strain BXSB producing accelerated autoimmunity and lymphoproliferation. Arthritis Rheum. 1979;22:1188–1194. - PubMed
-
- Pisitkun P, et al. Autoreactive B cell responses to RNA-related antigens due to TLR7 gene duplication. Science. 2006;312:1669–1672. - PubMed
-
- Parrish-Novak J, et al. Interleukin 21 and its receptor are involved in NK cell expansion and regulation of lymphocyte function. Nature. 2000;408:57–63. - PubMed
-
- Spolski R, Leonard WJ. Interleukin-21: Basic biology and implications for cancer and autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008;26:57–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

