RNA-directed DNA methylation induces transcriptional activation in plants
- PMID: 19164525
- PMCID: PMC2629447
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0809294106
RNA-directed DNA methylation induces transcriptional activation in plants
Abstract
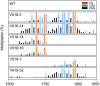
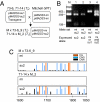
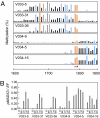
A class-C floral homeotic gene of Petunia, pMADS3, is specifically expressed in the stamen and carpels of developing flowers. We had previously reported the ect-pMADS3 phenomenon in which introduction of a part of the pMADS3 genomic sequence, including intron 2, induces ectopic expression of endogenous pMADS3. Unlike transcriptional or posttranscriptional gene silencing triggered by the introduction of homologous sequences, this observation is unique in that the gene expression is up-regulated. In this study, we demonstrated that the ect-pMADS3 phenomenon is due to transcriptional activation based on RNA-directed DNA methylation (RdDM) occurring in a particular CG in a putative cis-element in pMADS3 intron 2. The CG methylation was maintained over generations, along with pMADS3 ectopic expression, even in the absence of RNA triggers. These results demonstrate a previously undescribed transcriptional regulatory mechanism that could lead to the generation of a transcriptionally active epiallele, thereby contributing to plant evolution. Our results also reveal a putative negative cis-element for organ-specific transcriptional regulation of class-C floral homeotic genes, which could be difficult to identify by other approaches.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

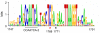
Similar articles
-
Transgene-triggered, epigenetically regulated ectopic expression of a flower homeotic gene pMADS3 in Petunia.Plant J. 2005 Sep;43(5):649-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02481.x. Plant J. 2005. PMID: 16115063
-
Role of petunia pMADS3 in determination of floral organ and meristem identity, as revealed by its loss of function.Plant J. 2002 Oct;32(1):115-27. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2002.01402.x. Plant J. 2002. PMID: 12366805
-
Ectopic expression of pMADS3 in transgenic petunia phenocopies the petunia blind mutant.Plant Cell. 1993 Aug;5(8):843-53. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.8.843. Plant Cell. 1993. PMID: 8104573 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-directed DNA methylation mediated by DRD1 and Pol IVb: a versatile pathway for transcriptional gene silencing in plants.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 May-Jun;1769(5-6):358-74. doi: 10.1016/j.bbaexp.2007.03.001. Epub 2007 Mar 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17449119 Review.
-
RNA-directed DNA methylation.Plant Mol Biol. 2000 Jun;43(2-3):203-20. doi: 10.1023/a:1006479327881. Plant Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10999405 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcription of DWARF4 plays a crucial role in auxin-regulated root elongation in addition to brassinosteroid homeostasis in Arabidopsis thaliana.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23851. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023851. Epub 2011 Aug 31. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21909364 Free PMC article.
-
The Underlying Nature of Epigenetic Variation: Origin, Establishment, and Regulatory Function of Plant Epialleles.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 10;22(16):8618. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168618. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide quantitative identification of DNA differentially methylated sites in Arabidopsis seedlings growing at different water potential.PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e59878. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059878. Epub 2013 Apr 8. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23577076 Free PMC article.
-
N4-acetyldeoxycytosine DNA modification marks euchromatin regions in Arabidopsis thaliana.Genome Biol. 2022 Jan 3;23(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s13059-021-02578-7. Genome Biol. 2022. PMID: 34980211 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental processes in the Rosaceae through the lens of DNA and RNA methylation.Planta. 2025 Feb 8;261(3):54. doi: 10.1007/s00425-025-04623-2. Planta. 2025. PMID: 39921711 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Matzke MA, Birchler JA. RNAi-mediated pathways in the nucleus. Nat Rev Genet. 2005;6:24–35. - PubMed
-
- Morris KV, Chan SW, Jacobsen SE, Looney DJ. Small interfering RNA-induced transcriptional gene silencing in human cells. Science. 2004;305:1289–1292. - PubMed
-
- Alleman M, et al. An RNA-dependent RNA polymerase is required for paramutation in maize. Nature. 2006;442:295–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

