Selective targeting of perivascular macrophages for clearance of beta-amyloid in cerebral amyloid angiopathy
- PMID: 19164591
- PMCID: PMC2633563
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0805453106
Selective targeting of perivascular macrophages for clearance of beta-amyloid in cerebral amyloid angiopathy
Abstract
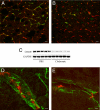
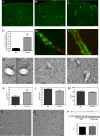
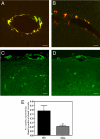
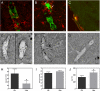
Cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA), the deposition of beta-amyloid (Abeta) peptides in leptomeningeal and cortical blood vessels, affects the majority of patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD). Evidence suggests that vascular amyloid deposits may result from impaired clearance of neuronal Abeta along perivascular spaces. We investigated the role of perivascular macrophages in regulating CAA severity in the TgCRND8 mouse model of AD. Depletion of perivascular macrophages significantly increased the number of thioflavin S-positive cortical blood vessels. ELISA confirmed that this increase was underscored by elevations in total vascular Abeta(42) levels. Conversely, stimulation of perivascular macrophage turnover reduced cerebral CAA load, an effect that was not mediated through clearance by microglia or astrocytes. These results highlight a function for the physiological role of perivascular macrophages in the regulation of CAA and suggest that selective targeting of perivascular macrophage activation might constitute a therapeutic strategy to clear vascular amyloid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Attems J, Lauda F, Jellinger KA. Unexpectedly low prevalence of intracerebral hemorrhages in sporadic cerebral amyloid angiopathy: an autopsy study. J Neurol. 2008;255:70–76. - PubMed
-
- Shin HK, et al. Age-dependent cerebrovascular dysfunction in a transgenic mouse model of cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Brain. 2007;130:2310–2319. - PubMed
-
- Perlmutter LS. Microvascular pathology and vascular basement membrane components in Alzheimer's disease. Mol Neurobiol. 1994;9:33–40. - PubMed
-
- Tian J, et al. Relationships in Alzheimer's disease between the extent of Abeta deposition in cerebral blood vessel walls, as cerebral amyloid angiopathy, and the amount of cerebrovascular smooth muscle cells and collagen. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2006;32:332–340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

