Image-guided, noninvasive, spatiotemporal control of gene expression
- PMID: 19164593
- PMCID: PMC2633569
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0806936106
Image-guided, noninvasive, spatiotemporal control of gene expression
Abstract
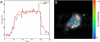
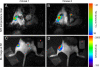
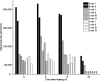
Spatiotemporal control of transgene expression is of paramount importance in gene therapy. Here, we demonstrate the use of magnetic resonance temperature imaging (MRI)-guided, high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) in combination with a heat-inducible promoter [heat shock protein 70 (HSP70)] for the in vivo spatiotemporal control of transgene activation. Local gene activation induced by moderate hyperthermia in a transgenic mouse expressing luciferase under the control of the HSP70 promoter showed a high similarity between the local temperature distribution in vivo and the region emitting light. Modulation of gene expression is possible by changing temperature, duration, and location of regional heating. Mild heating protocols (2 min at 43 degrees C) causing no tissue damage were sufficient for significant gene activation. The HSP70 promoter was shown to be induced by the local temperature increase and not by the mechanical effects of ultrasound. Therefore, the combination of MRI-guided HIFU heating and transgenes under control of heat-inducible HSP promoter provides a direct, noninvasive, spatial control of gene expression via local hyperthermia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Vilaboa N, Voellmy R. Regulatable gene expression systems for gene therapy. Curr Gene Ther. 2006;6:421–438. - PubMed
-
- Gorski K, Carneiro M, Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986;47:767–776. - PubMed
-
- Melo LG, et al. Endothelium-targeted gene and cell-based therapies for cardiovascular disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004;24:1761–1774. - PubMed
-
- Rendahl KG, et al. Regulation of gene expression in vivo following transduction by two separate rAAV vectors. Nat Biotechnol. 1998;16:757–761. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, DeMayo FJ, Tsai SY, O'Malley BW. Ligand-inducible and liver-specific target gene expression in transgenic mice. Nat Biotechnol. 1997;15:239–243. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

