Computational simulations of the early steps of protein aggregation
- PMID: 19164927
- PMCID: PMC2633700
- DOI: 10.4161/pri.1.1.3969
Computational simulations of the early steps of protein aggregation
Abstract
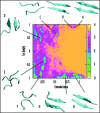
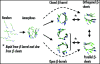
There is strong evidence that the oligomers of key proteins, formed during the early steps of aggregation, could be the primary toxic species associated with human neuro-degenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's and prion diseases. Here, we review recent progress in the development of computational approaches in order to understand the structures, dynamics and free energy surfaces of oligomers. We also discuss possible research directions for the coming years.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protein misfolding and prion diseases.J Mol Biol. 1999 Oct 22;293(2):313-20. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.2990. J Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10550211 Review.
-
Amyloids, prions and the inherent infectious nature of misfolded protein aggregates.Trends Biochem Sci. 2006 Mar;31(3):150-5. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2006.01.002. Epub 2006 Feb 13. Trends Biochem Sci. 2006. PMID: 16473510 Review.
-
Prion protein interconversions and the transmissible spongiform encephalopathies.Structure. 1999 Oct 15;7(10):R231-40. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(00)80049-0. Structure. 1999. PMID: 10545332 Review.
-
The Unexposed Secrets of Prion Protein Oligomers.J Mol Neurosci. 2015 Aug;56(4):932-937. doi: 10.1007/s12031-015-0546-1. Epub 2015 Apr 1. J Mol Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25823438 Review.
-
Delineating common molecular mechanisms in Alzheimer's and prion diseases.Trends Biochem Sci. 2006 Aug;31(8):465-72. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2006.06.006. Epub 2006 Jul 3. Trends Biochem Sci. 2006. PMID: 16820299 Review.
Cited by
-
Conformational dynamics of amyloid-β (16-22) peptide in aqueous ionic liquids.RSC Adv. 2020 Sep 8;10(55):33248-33260. doi: 10.1039/d0ra06609e. eCollection 2020 Sep 7. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35515066 Free PMC article.
-
Structures of beta-amyloid peptide 1-40, 1-42, and 1-55-the 672-726 fragment of APP-in a membrane environment with implications for interactions with gamma-secretase.J Am Chem Soc. 2009 Dec 16;131(49):17843-52. doi: 10.1021/ja905457d. J Am Chem Soc. 2009. PMID: 19995075 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of All-Atom Molecular Mechanics Force Fields on Amyloid Peptide Assembly: The Case of Aβ16-22 Dimer.J Chem Theory Comput. 2019 Feb 12;15(2):1440-1452. doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.8b01107. Epub 2019 Jan 28. J Chem Theory Comput. 2019. PMID: 30633867 Free PMC article.
-
The OPEP protein model: from single molecules, amyloid formation, crowding and hydrodynamics to DNA/RNA systems.Chem Soc Rev. 2014 Jul 7;43(13):4871-93. doi: 10.1039/c4cs00048j. Epub 2014 Apr 23. Chem Soc Rev. 2014. PMID: 24759934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure and dynamics of amyloid-β segmental polymorphisms.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41479. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041479. Epub 2012 Jul 24. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22911797 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Selkoe DJ. The cell biology of beta-amyloid precursor protein and presenilin in Alzheimer's disease. Trends Cell Biol. 1998;7:447–453. - PubMed
-
- Gejyo F, Homma N, Suzuki Y, Arakawa M. Serum levels of beta 2-microglobulin as a new form of amyloid protein in patients undergoing long-term hemodialysis. New Engl J Med. 1986;314:585–586. - PubMed
-
- Legname G, Baskakov IV, Nguyen HO, Riesner D, Cohen FE, DeArmond SJ, Prusiner SB. Synthetic mammalian prions. Science. 2004;305:673–676. - PubMed
-
- Hou L, Shao H, Zhang Y, Li H, Menon NK, Neuhaus EB, Brewer JM, Byeon IJ, Ray DG, Vitek MP, Iwashita T, Makula RA, Przybyla AB, Zagorski MG. Solution NMR studies of the Abeta(1–40) and Abeta(1–42) peptides establish that the Met35 oxidation state affects the mechanism of amyloid formation. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:1992–2005. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
