Terminal Continuation (TC) RNA amplification enables expression profiling using minute RNA input obtained from mouse brain
- PMID: 19165351
- PMCID: PMC2629436
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms9112091
Terminal Continuation (TC) RNA amplification enables expression profiling using minute RNA input obtained from mouse brain
Abstract
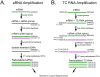
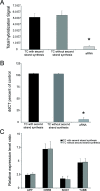
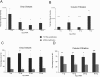
A novel methodology named terminal continuation (TC) RNA amplification has been developed to amplify RNA from minute amounts of starting material. Utility of the TC RNA amplification method is demonstrated with two new modifications including obviating the need for second strand synthesis, and purifying the amplification template using column filtration prior to in vitro transcription (IVT). Using four low concentrations of RNA extracted from mouse brain (1, 10, 25 and 50 ng), one round TC RNA amplification was compared to one round amplified antisense RNA (aRNA) in conjunction with column filtration and drop dialysis purification. The TC RNA amplification without second strand synthesis performed extremely well on custom-designed cDNA array platforms, and column filtration was found to provide higher positive detection of individual clones when hybridization signal intensity was subtracted from corresponding negative control hybridization signal levels. Results indicate that TC RNA amplification without second strand synthesis, in conjunction with column filtration, is an excellent method for RNA amplification from extremely small amounts of input RNA from mouse brain and postmortem human brain, and is compatible with microaspiration strategies and subsequent microarray analysis.
Keywords: TC RNA amplification; aRNA; brain extract; column filtration; in vitro transcription; microarray.
Figures


References
-
- Sambrook J, Russell DW. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. 3rd Ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA: 2001.
-
- Kacharmina JE, Crino PB, Eberwine J. Preparation of cDNA from single cells and subcellular regions. Methods Enzymol. 1999;303:3–18. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

