Quantitative magnetization transfer measured pool-size ratio reflects optic nerve myelin content in ex vivo mice
- PMID: 19165898
- PMCID: PMC2632728
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.21850
Quantitative magnetization transfer measured pool-size ratio reflects optic nerve myelin content in ex vivo mice
Abstract
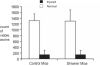
Optic nerves from mice that have undergone retinal ischemia were examined using a newly implemented quantitative magnetization transfer (qMT) technique. Previously published results indicate that the optic nerve from retinal ischemia mice suffered significant axon degeneration without detectable myelin injury at 3 days after reperfusion. At this time point, we acquired ex vivo qMT parameters from both shiverer mice (which have nearly no myelin) and control mice that have undergone retinal ischemia, and these qMT measures were compared with diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) results. Our findings suggests that the qMT estimated ratio of the pool sizes of the macromolecular and free water protons reflected the different myelin contents in the optic nerves between the shiverer and control mice. This pool size ratio was specific to myelin content only and was not significantly affected by the presence of axon injury in mouse optic nerve 3 days after retinal ischemia.
Copyright 2009 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Dousset V, Grossman RI, Ramer KN, Schnall MD, Young LH, Gonzalezscarano F, Lavi E, Cohen JA. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis and multiple sclerosis - lesion characterization with magnetization transfer imaging. Radiology. 1992;182(2):483–491. - PubMed
-
- Filippi M, Cercignani M, Inglese M, Horsfield MA, Comi G. Diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 2001;56(3):304–311. - PubMed
-
- Mackay A, Whittall K, Adler J, Li D, Paty D, Graeb D. In-vivo visualization of myelin water in brain by magnetic resonance. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 1994;31(6):673–677. - PubMed
-
- Kim JH, Budde MD, Liang HF, Klein RS, Russell JH, Cross AH, Song SK. Detecting axon damage in spinal cord from a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Neurobiol Dis. 2006;21(3):626–632. - PubMed
-
- Song SK, Sun SW, Ramsbottom MJ, Chang C, Russell J, Cross AH. Dysmyelination revealed through MRI as increased radial (but unchanged axial) diffusion of water. Neuroimage. 2002;17(3):1429–1436. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

