Genetic variants near TNFAIP3 on 6q23 are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 19165918
- PMCID: PMC2772171
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.200
Genetic variants near TNFAIP3 on 6q23 are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
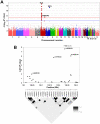
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease influenced by genetic and environmental factors. We carried out a genome-wide association scan and replication study and found an association between SLE and a variant in TNFAIP3 (rs5029939, meta-analysis P = 2.89 x 10(-12), OR = 2.29). We also found evidence of two independent signals near TNFAIP3 associated with SLE, including one previously associated with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). These results establish that variants near TNFAIP3 contribute to differential risk of SLE and RA.
Figures
References
-
- Helmick CG, et al. Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and other rheumatic conditions in the United States: Part I. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58:15–25. - PubMed
-
- Kaslow RA, Masi AT. Age, sex, and race effects on mortality from systemic lupus erythematosus in the United States. Arthritis Rheum. 1978;21:473–9. - PubMed
-
- Boone DL, et al. The ubiquitin-modifying enzyme A20 is required for termination of Toll-like receptor responses. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:1052–60. - PubMed
-
- Wertz IE, et al. De-ubiquitination and ubiquitin ligase domains of A20 downregulate NF-kappaB signalling. Nature. 2004;430:694–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R56 AI063274/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR053483/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- MH067257/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 5F32AR50927/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060870/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059587/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH060879/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH059588/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH59566/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR056768/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- MH59587/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH061675/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH061675/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI063274/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F32 AR050927/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- MH 63420/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH60870/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH59586/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 076113/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- AR043247/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR052125/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AR002105/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR052125/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI063274/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH067257/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059571/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059565/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH059565/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059586/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059566/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 MH063420/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059588/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR043274/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060879/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

