Deletion polymorphism upstream of IRGM associated with altered IRGM expression and Crohn's disease
- PMID: 19165925
- PMCID: PMC2731799
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.215
Deletion polymorphism upstream of IRGM associated with altered IRGM expression and Crohn's disease
Abstract
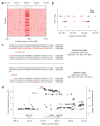
Following recent success in genome-wide association studies, a critical focus of human genetics is to understand how genetic variation at implicated loci influences cellular and disease processes. Crohn's disease (CD) is associated with SNPs around IRGM, but coding-sequence variation has been excluded as a source of this association. We identified a common, 20-kb deletion polymorphism, immediately upstream of IRGM and in perfect linkage disequilibrium (r2 = 1.0) with the most strongly CD-associated SNP, that causes IRGM to segregate in the population with two distinct upstream sequences. The deletion (CD risk) and reference (CD protective) haplotypes of IRGM showed distinct expression patterns. Manipulation of IRGM expression levels modulated cellular autophagy of internalized bacteria, a process implicated in CD. These results suggest that the CD association at IRGM arises from an alteration in IRGM regulation that affects the efficacy of autophagy and identify a common deletion polymorphism as a likely causal variant.
Figures


Comment in
-
Going with the flow of autophagy in Crohn's disease: IRGM risk polymorphism found upstream.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2010 Jan;16(1):179-80. doi: 10.1002/ibd.21063. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2010. PMID: 19714746 No abstract available.
References
-
- Singh SB, Davis AS, Taylor GA, Deretic V. Human IRGM induces autophagy to eliminate intracellular mycobacteria. Science. 2006;313:1438–1441. - PubMed
-
- Hampe J, et al. A genome-wide association scan of nonsynonymous SNPs identifies a susceptibility variant for Crohn disease in ATG16L1. Nat Genet. 2007;39:207–211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI062773/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK040561/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK62413/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062413/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK043351/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK062429/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK064869/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK62431/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062432/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK43351/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK064869/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062429/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062422/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK62422/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL088297/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI062773/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062423/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL088297/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK62432/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK62429/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK62420/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK083756/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK62423/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062420/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062431/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

