MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions
- PMID: 19167326
- PMCID: PMC3794896
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.002
MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions
Abstract
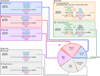
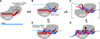
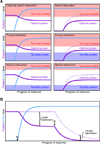
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenous approximately 23 nt RNAs that play important gene-regulatory roles in animals and plants by pairing to the mRNAs of protein-coding genes to direct their posttranscriptional repression. This review outlines the current understanding of miRNA target recognition in animals and discusses the widespread impact of miRNAs on both the expression and evolution of protein-coding genes.
Figures


References
-
- Abelson JF, Kwan KY, O'Roak BJ, Baek DY, Stillman AA, Morgan TM, Mathews CA, Pauls DL, Rasin MR, Gunel M, et al. Sequence variants in SLITRK1 are associated with Tourette's syndrome. Science. 2005;310:317–320. - PubMed
-
- Abrahante JE, Daul AL, Li M, Volk ML, Tennessen JM, Miller EA, Rougvie AE. The Caenorhabditis elegans hunchback-like gene lin-57/hbl-1 controls developmental time and is regulated by microRNAs. Dev Cell. 2003;4:625–637. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V, Lee RC, Lavanway A, Williams PT, Jewell D. MicroRNAs and other tiny endogenous RNAs in C. elegans . Curr Biol. 2003;13:807–818. - PubMed
-
- Ameres SL, Martinez J, Schroeder R. Molecular basis for target RNA recognition and cleavage by human RISC. Cell. 2007;130:101–112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

