Murine neonatal recent thymic emigrants are phenotypically and functionally distinct from adult recent thymic emigrants
- PMID: 19168791
- PMCID: PMC2689058
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2008-08-173658
Murine neonatal recent thymic emigrants are phenotypically and functionally distinct from adult recent thymic emigrants
Abstract
In contrast to adults, the murine neonatal CD4+ compartment contains a high frequency of recent thymic emigrants (RTEs). However, the functional capabilities of these cells in neonates are relatively unknown. Moreover, it has not been determined whether RTEs from neonates and adults are comparable. Here we have directly compared neonatal and adult CD4+ RTEs for the first time, using a transgenic mouse strain that allows for the identification and purification of RTEs. Our data demonstrate that RTEs from murine neonates and adults are phenotypically and functionally distinct. In particular, although the magnitude of RTEs cytokine responses from both age groups is dependent on the conditions of activation, neonatal RTEs always exhibited higher levels of effector Th1/Th2 cytokine production than adult RTEs. In addition, neonatal, but not adult, RTEs showed early proliferation in response to stimulation with interleukin-7 alone. This was associated with faster kinetics of interleukin-7Ralpha down-regulation and higher levels of pSTAT5 in neonatal RTEs. These quantitative and qualitative differences in the neonatal and adult RTEs populations may at least partially explain the diverse responses that are elicited in vivo in neonates in response to different conditions of antigen exposure.
Figures
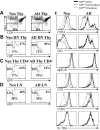
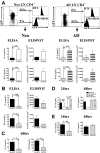




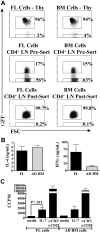
Comment in
-
RTEs: lazy T-cell teenagers.Blood. 2009 May 28;113(22):5374-5. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-03-207308. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19478052 No abstract available.
References
-
- Adkins B, Leclerc C, Marshall-Clarke S. Neonatal adaptive immunity comes of age. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:553–564. - PubMed
-
- Scollay RG, Butcher EC, Weissman IL. Thymus cell migration: quantitative aspects of cellular traffic from the thymus to the periphery in mice. Eur J Immunol. 1980;10:210–218. - PubMed
-
- Boursalian TE, Golob J, Soper DM, Cooper CJ, Fink PJ. Continued maturation of thymic emigrants in the periphery. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:418–425. - PubMed
-
- Luettig B, Sponholz A, Heerwagen C, Bode U, Westermann J. Recent thymic emigrants (CD4+) continuously migrate through lymphoid organs: within the tissue they alter surface molecule expression. Scand J Immunol. 2001;53:563–571. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

