Hedgehog signalling is essential for maintenance of cancer stem cells in myeloid leukaemia
- PMID: 19169242
- PMCID: PMC2946231
- DOI: 10.1038/nature07737
Hedgehog signalling is essential for maintenance of cancer stem cells in myeloid leukaemia
Erratum in
- Nature. 2009 Jul 30;460(7255):652
Abstract
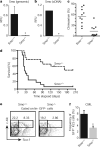
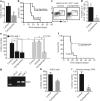
Although the role of Hedgehog (Hh) signalling in embryonic pattern formation is well established, its functions in adult tissue renewal and maintenance remain unclear, and the relationship of these functions to cancer development has not been determined. Here we show that the loss of Smoothened (Smo), an essential component of the Hh pathway, impairs haematopoietic stem cell renewal and decreases induction of chronic myelogenous leukaemia (CML) by the BCR-ABL1 oncoprotein. Loss of Smo causes depletion of CML stem cells--the cells that propagate the leukaemia--whereas constitutively active Smo augments CML stem cell number and accelerates disease. As a possible mechanism for Smo action, we show that the cell fate determinant Numb, which depletes CML stem cells, is increased in the absence of Smo activity. Furthermore, pharmacological inhibition of Hh signalling impairs not only the propagation of CML driven by wild-type BCR-ABL1, but also the growth of imatinib-resistant mouse and human CML. These data indicate that Hh pathway activity is required for maintenance of normal and neoplastic stem cells of the haematopoietic system and raise the possibility that the drug resistance and disease recurrence associated with imatinib treatment of CML might be avoided by targeting this essential stem cell maintenance pathway.
Figures


References
-
- Ingham PW, Placzek M. Orchestrating ontogenesis: variations on a theme by sonic hedgehog. Nature Rev. Genet. 2006;7:841–850. - PubMed
-
- Rohatgi R, Scott MP. Patching the gaps in Hedgehog signalling. Nature Cell Biol. 2007;9:1005–1009. - PubMed
-
- Ren R. Mechanisms of BCR–ABL in the pathogenesis of chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Nature Rev. Cancer. 2005;5:172–183. - PubMed
-
- Gorre ME, et al. Clinical resistance to STI-571 cancer therapy caused by BCRABL gene mutation or amplification. Science. 2001;293:876–880. - PubMed
-
- Graham SM, et al. Primitive, quiescent, Philadelphia-positive stem cells from patients with chronic myeloid leukemia are insensitive to STI571 in vitro. Blood. 2002;99:319–325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

