Genome-wide scan reveals association of psoriasis with IL-23 and NF-kappaB pathways
- PMID: 19169254
- PMCID: PMC2745122
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.311
Genome-wide scan reveals association of psoriasis with IL-23 and NF-kappaB pathways
Abstract
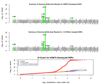
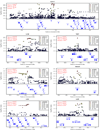
Psoriasis is a common immune-mediated disorder that affects the skin, nails and joints. To identify psoriasis susceptibility loci, we genotyped 438,670 SNPs in 1,409 psoriasis cases and 1,436 controls of European ancestry. We followed up 21 promising SNPs in 5,048 psoriasis cases and 5,041 controls. Our results provide strong support for the association of at least seven genetic loci and psoriasis (each with combined P < 5 x 10(-8)). Loci with confirmed association include HLA-C, three genes involved in IL-23 signaling (IL23A, IL23R, IL12B), two genes that act downstream of TNF-alpha and regulate NF-kappaB signaling (TNIP1, TNFAIP3) and two genes involved in the modulation of Th2 immune responses (IL4, IL13). Although the proteins encoded in these loci are known to interact biologically, we found no evidence for epistasis between associated SNPs. Our results expand the catalog of genetic loci implicated in psoriasis susceptibility and suggest priority targets for study in other auto-immune disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
ABB and SJS own stock and/or stock options in Celera Corporation.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

