Compound FLZ inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory effects via down-regulation of the TAK-IKK and TAK-JNK/p38MAPK pathways in RAW264.7 macrophages
- PMID: 19169268
- PMCID: PMC4002472
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2008.29
Compound FLZ inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory effects via down-regulation of the TAK-IKK and TAK-JNK/p38MAPK pathways in RAW264.7 macrophages
Abstract
Aim: The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of the squamosamide derivative FLZ (N-2-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-ethyl-2-(2,5-dimethoxy-phenyl)-3-(3-methoxy-4-hydroxy-phenyl)-acrylamide) on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory mediator production and the underlying mechanism in RAW264.7 macrophages.
Methods: RAW264.7 cells were preincubated with non-toxic concentrations of compound FLZ (1, 5, and 10 micromol/L) for 30 min and then stimulated with 10 microg/L LPS. The production of nitric oxide (NO), the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2), and the activation of nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-kappaB) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways were examined.
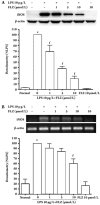
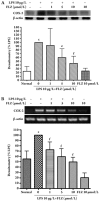
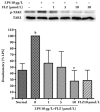
Results: FLZ significantly inhibited the LPS-induced production of NO, as well as the expression of iNOS and COX-2 at both the RNA and the protein levels in RAW264.7 cells. The LPS-induced increase in the DNA binding activity of NF-kappaB and activator protein 1 (AP-1), the nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB p65, the degradation of the inhibitory kappaBalpha protein (IkappaBalpha) and the phosphorylation of IkappaBalpha, IkappaB kinase (IKK) alpha/beta, c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38 MAPKs were all suppressed by FLZ. However, the phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) was not affected. Further study revealed that FLZ inhibited the phosphorylation of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta)-activated kinase 1 (TAK1), which is an upstream signaling molecule required for IKKalpha/beta, JNK and p38 activation.
Conclusion: FLZ inhibited the LPS-induced production of inflammatory mediators at least partly through the downregulation of the TAK-IKK and TAK-JNK/p38MAPK pathways.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Methyl-1-hydroxy-2-naphthoate, a novel naphthol derivative, inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in macrophages via suppression of NF-κB, JNK and p38 MAPK pathways.Inflamm Res. 2011 Sep;60(9):851-9. doi: 10.1007/s00011-011-0345-2. Epub 2011 Jun 11. Inflamm Res. 2011. PMID: 21667204
-
Euscaphic acid isolated from roots of Rosa rugosa inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory responses via TLR4-mediated NF-κB inactivation in RAW 264.7 macrophages.J Cell Biochem. 2012 Jun;113(6):1936-46. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24062. J Cell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22234926
-
Xanthii fructus inhibits inflammatory responses in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages through suppressing NF-κB and JNK/p38 MAPK.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Dec 24;176:394-401. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.11.020. Epub 2015 Nov 10. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26560439
-
Crosstalk between phytochemicals and inflammatory signaling pathways.Inflammopharmacology. 2023 Jun;31(3):1117-1147. doi: 10.1007/s10787-023-01206-z. Epub 2023 Apr 6. Inflammopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 37022574 Review.
-
IκB kinase regulation of the TPL-2/ERK MAPK pathway.Immunol Rev. 2012 Mar;246(1):168-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2012.01104.x. Immunol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22435554 Review.
Cited by
-
Mungbean seed coat water extract inhibits inflammation in LPS-induced acute liver injury mice and LPS-stimulated RAW 246.7 macrophages via the inhibition of TAK1/IκBα/NF-κB.J Food Sci Technol. 2020 Jul;57(7):2659-2668. doi: 10.1007/s13197-020-04302-y. Epub 2020 Feb 26. J Food Sci Technol. 2020. PMID: 32549616 Free PMC article.
-
Data on eleven sesquiterpenoids from the cultured mycelia of Ganoderma capense.Data Brief. 2017 Apr 19;12:361-363. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2017.04.012. eCollection 2017 Jun. Data Brief. 2017. PMID: 28491940 Free PMC article.
-
An in vivo microdialysis study of FLZ penetration through the blood-brain barrier in normal and 6-hydroxydopamine induced Parkinson's disease model rats.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:850493. doi: 10.1155/2014/850493. Epub 2014 Jun 23. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25045708 Free PMC article.
-
Squamosamide derivative FLZ inhibits TNF-α-induced ICAM-1 expression via down-regulation of the NF-κB signaling pathway in ARPE-19 cells.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Aug 1;8(8):9126-32. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26464656 Free PMC article.
-
Polydatin ameliorates Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis in mice via inhibiting TLR2-mediated activation of the p38 MAPK/NF-κB pathway.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2017 Feb;38(2):211-222. doi: 10.1038/aps.2016.123. Epub 2016 Nov 28. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2017. PMID: 27890916 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xie P, Jiao XZ, Liang XT, Feng WH, Wei HL, Liu GT.Synthesis and antioxiactivity of squamosamide cyclic analogs Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao 200426372–8.Chinese. - PubMed
-
- Zhang D, Zhang JJ, Liu GT. The novel squamosamide derivative FLZ protects against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced apoptosis through inhibition of related signal transduction in SH-SY5Y cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007;561:1–6. - PubMed
-
- Zhang D, Zhang JJ, Liu GT. The novel squamosamide derivative (compound FLZ) attenuated 1-methyl-4-phenyl-pyridinium ion (MPP+)-induced apoptosis and alternations of related signal transduction in SH-SY5Y cells. Neuropharmacology. 2007;52:423–9. - PubMed
-
- Fang F, Liu GT. Novel squamosamide derivative (compound FLZ) attenuates Abeta(25–35)-induced toxicity in SH-SY5Y cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2008;29:152–60. - PubMed
-
- Fang F, Liu GT. Protective effects of compound FLZ on beta-amyloid peptide-(25–35)-induced mouse hippocampal injury and learning and memory impairment. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2006;27:651–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

