Phytoestrogens regulate mRNA and protein levels of guanine nucleotide-binding protein, beta-1 subunit (GNB1) in MCF-7 cells
- PMID: 19170076
- PMCID: PMC4547522
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.21699
Phytoestrogens regulate mRNA and protein levels of guanine nucleotide-binding protein, beta-1 subunit (GNB1) in MCF-7 cells
Abstract
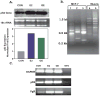
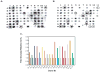
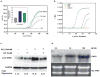
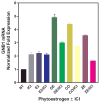
Phytoestrogens (PEs) are non-steroidal ligands, which regulate the expression of number of estrogen receptor-dependent genes responsible for a variety of biological processes. Deciphering the molecular mechanism of action of these compounds is of great importance because it would increase our understanding of the role(s) these bioactive chemicals play in prevention and treatment of estrogen-based diseases. In this study, we applied suppression subtractive hybridization (SSH) to identify genes that are regulated by PEs through either the classic nuclear-based estrogen receptor or membrane-based estrogen receptor pathways. SSH, using mRNA from genistein (GE) treated MCF-7 cells as testers, resulted in a significant increase in GNB1 mRNA expression levels as compared with 10 nM 17beta estradiol or the no treatment control. GNB1 mRNA expression was up regulated two- to fivefold following exposure to 100.0 nM GE. Similarly, GNB1 protein expression was up regulated 12- to 14-fold. GE regulation of GNB1 was estrogen receptor-dependent, in the presence of the anti-estrogen ICI-182,780, both GNB1 mRNA and protein expression were inhibited. Analysis of the GNB1 promoter using ChIP assay showed a PE-dependent association of estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) and beta (ERbeta) to the GNB1 promoter. This association was specific for ERalpha since association was not observed when the cells were co-incubated with GE and the ERalpha antagonist, ICI. Our data demonstrate that the levels of G-protein, beta-1 subunit are regulated by PEs through an estrogen receptor pathway and further suggest that PEs may control the ratio of alpha-subunit to beta/gamma-subunits of the G-protein complex in cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 219: 584-594, 2009. (c) 2009 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Adlercreutz H, Bannwart C, Wahala K, Makela T, Brunow G, Hase T, Arosemena PJ, Kellis JT, Jr, Vickery LE. Inhibition of human aromatase by mammalian lignans and isoflavonoid phytoestrogens. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1993;44(2):147–153. - PubMed
-
- Ahn CH, Jeong EG, Lee JW, Kim MS, Kim SH, Kim SS, Yoo NJ, Lee SH. Expression of beclin-1, an autophagy-related protein, in gastric and colorectal cancers. Apmis. 2007;115(12):1344–1349. - PubMed
-
- Allred CD, Ju YH, Allred KF, Chang J, Helferich WG. Dietary genistin stimulates growth of estrogen-dependent breast cancer tumors similar to that observed with genistein. Carcinogenesis. 2001;22(10):1667–1673. - PubMed
-
- Ansonoff MA, Etgen AM. βββ elevates protein kinase C catalytic activity in the preoptic area of female rats. Endocrinology. 1998;139(7):3050–3056. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

