Mitochondrial localization, ELK-1 transcriptional regulation and growth inhibitory functions of BRCA1, BRCA1a, and BRCA1b proteins
- PMID: 19170108
- PMCID: PMC3693557
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.21708
Mitochondrial localization, ELK-1 transcriptional regulation and growth inhibitory functions of BRCA1, BRCA1a, and BRCA1b proteins
Abstract
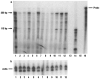
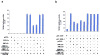
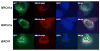
BRCA1 is a tumor suppressor gene that is mutated in families with breast and ovarian cancer. Several BRCA1 splice variants are found in different tissues, but their subcellular localization and functions are poorly understood at the moment. We previously described BRCA1 splice variant BRCA1a to induce apoptosis and function as a tumor suppressor of triple negative breast, ovarian and prostate cancers. In this study we have analyzed the function of BRCA1 isoforms (BRCA1a and BRCA1b) and compared them to the wild-type BRCA1 protein using several criteria like studying expression in normal and tumor cells by RNase protection assays, subcellular localization/fractionation by immunofluorescence microscopy and Western blot analysis, transcription regulation of biological relevant proteins and growth suppression in breast cancer cells. We are demonstrating for the first time that ectopically expressed GFP-tagged BRCA1, BRCA1a, and BRCA1b proteins are localized to the mitochondria, repress ELK-1 transcriptional activity and possess antiproliferative activity on breast cancer cells. These results suggest that the exon 9, 10, and 11 sequences (aa 263-1365) which contain two nuclear localization signals, p53, Rb, c-Myc, gamma-tubulin, Stat, Rad51, Rad50 binding domains, angiopoietin-1 repression domain are not absolutely required for mitochondrial localization and growth suppressor function of these proteins. Since mitochondrial dysfunction is a hallmark of cancer, we can speculate that the mitochondrial localization of BRCA1 proteins may be functionally significant in regulating both the mitochondrial DNA damage as well as apoptotic activity of BRCA1 proteins and mislocalization causes cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 219: 634-641, 2009. (c) 2009 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures






References
-
- Anderson S, Schlegel BP, Nakajima T, Wolpin ES, Parvin JD. BRCA1 protein is linked to the RNA polymerase II holoenzyme complex via RNA helicase A. Nat Genet. 1998;19:254–256. - PubMed
-
- Au W, Henderson BR. The BRCA1 RING and BRCT domains cooperate in targeting BRCA1 to ionizing radiation-induced nuclear foci. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:6993–7001. - PubMed
-
- Bianchi N, Bianchi MS, Richard SM. Mitochondrial genome instability in human cancers. Mutant Res. 2001;488:9–23. - PubMed
-
- Boulton S. Cellular functions of the BRCA1 tumor-suppressor proteins. Biochem SOC Trans. 2006;34:633–645. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

