Threonine phosphorylation prevents promoter DNA binding of the Group B Streptococcus response regulator CovR
- PMID: 19170889
- PMCID: PMC3133594
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06616.x
Threonine phosphorylation prevents promoter DNA binding of the Group B Streptococcus response regulator CovR
Abstract
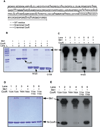
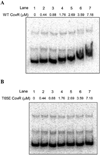
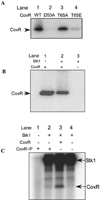
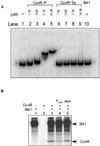
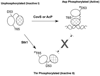
All living organisms communicate with the external environment for their survival and existence. In prokaryotes, communication is achieved by two-component systems (TCS) comprising histidine kinases and response regulators. In eukaryotes, signalling is accomplished by serine/threonine and tyrosine kinases. Although TCS and serine/threonine kinases coexist in prokaryotes, direct cross-talk between these families was first described in Group B Streptococcus (GBS). A serine/threonine kinase (Stk1) and a TCS (CovR/CovS) co-regulate toxin expression in GBS. Typically, promoter binding of regulators like CovR is controlled by phosphorylation of the conserved active site aspartate (D53). In this study, we show that Stk1 phosphorylates CovR at threonine 65. The functional consequence of threonine phosphorylation of CovR in GBS was evaluated using phosphomimetic and silencing substitutions. GBS encoding the phosphomimetic T65E allele are deficient for CovR regulation unlike strains encoding the non-phosphorylated T65A allele. Further, compared with wild-type or T65A CovR, the T65E CovR is unable to bind promoter DNA and is decreased for phosphorylation at D53, similar to Stk1-phosphorylated CovR. Collectively, we provide evidence for a novel mechanism of response regulator control that enables GBS (and possibly other prokaryotes) to fine-tune gene expression for environmental adaptation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulation of cytotoxin expression by converging eukaryotic-type and two-component signalling mechanisms in Streptococcus agalactiae.Mol Microbiol. 2006 Nov;62(4):941-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05431.x. Epub 2006 Sep 27. Mol Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 17005013 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-site phosphorylation of the control of virulence regulator impacts group a streptococcal global gene expression and pathogenesis.PLoS Pathog. 2014 May 1;10(5):e1004088. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004088. eCollection 2014 May. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24788524 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of CovR expression in Group B Streptococcus impacts blood-brain barrier penetration.Mol Microbiol. 2010 Jul;77(2):431-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07215.x. Epub 2010 May 19. Mol Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20497331 Free PMC article.
-
Serine/threonine/tyrosine phosphorylation regulates DNA binding of bacterial transcriptional regulators.Microbiology (Reading). 2015 Sep;161(9):1720-1729. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000148. Epub 2015 Jul 23. Microbiology (Reading). 2015. PMID: 26220449 Review.
-
The two faces of Janus: virulence gene regulation by CovR/S in group A streptococci.Mol Microbiol. 2007 Apr;64(1):34-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05649.x. Mol Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17376070 Review.
Cited by
-
Reciprocal regulation of cephalosporin resistance in Enterococcus faecalis.mBio. 2011 Nov 1;2(6):e00199-11. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00199-11. Print 2011. mBio. 2011. PMID: 22045988 Free PMC article.
-
Group B streptococcal infections in pregnancy and early life.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2025 Mar 13;38(1):e0015422. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00154-22. Epub 2024 Nov 25. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2025. PMID: 39584819 Review.
-
Regulation of prokaryotic gene expression by eukaryotic-like enzymes.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2012 Apr;15(2):125-31. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2011.12.006. Epub 2012 Jan 3. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22221896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Double Life of Group B Streptococcus: Asymptomatic Colonizer and Potent Pathogen.J Mol Biol. 2019 Jul 26;431(16):2914-2931. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.01.035. Epub 2019 Jan 31. J Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30711542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ser/Thr phosphorylation as a regulatory mechanism in bacteria.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2015 Apr;24:47-52. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2015.01.005. Epub 2015 Jan 24. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25625314 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aitken A. Protein consensus sequence motifs. Methods Mol Biol. 2003;211:465–485. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. New York: John Wiley & Sons; 1997.
-
- Baker CJ, Edwards MW. Group B streptococcal infections. In: Remington JS, Klein JO, editors. Infectious Diseases of the Fetus and Newborn Infant. Philadelphia, PA: W.B. Saunders; 1995. pp. 980–1054.
-
- Barz C, Abahji TN, Trulzsch K, Heesemann J. The Yersinia Ser/Thr protein kinase YpkA/YopO directly interacts with the small GTPases RhoA and Rac-1. FEBS Lett. 2000;482:139–143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

