Nonlinear absorption microscopy
- PMID: 19170931
- PMCID: PMC7341902
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.2008.00514.x
Nonlinear absorption microscopy
Abstract
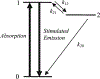
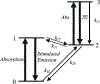
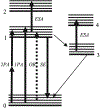
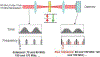
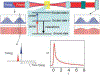
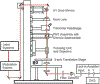
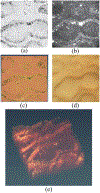
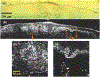
For the past two decades, nonlinear microscopy has been developed to overcome the scattering problem in thick tissue imaging. Owing to its increased imaging depth and high spatial resolution, nonlinear microscopy becomes the first choice for imaging living tissues. The use of nonlinear optical effects not only facilitates the signal originating from an extremely small volume defined by light focusing but also provides novel contrast mechanisms with molecular specificity. Nonlinear absorption is a nonlinear optical effect in which the absorption coefficient depends on excitation intensity. As a commonly used spectroscopy tool, nonlinear absorption measurement uncovers many photophysical and photochemical processes correlated with electronic states of molecules. Recently we have been focusing on adapting this spectroscopy method to a microscopy imaging technique. The effort leads to a novel modality in nonlinear microscopy-nonlinear absorption microscopy. This article summarizes the principles and instrumentation of this imaging technique and highlights some of the recent progress in applying it to imaging skin pigmentation and microvasculature under ex vivo or in vivo conditions.
Figures

References
-
- Epstein RJ (2002) Human Molecular Biology: An Introduction to the Molecular Basis of Health and Disease. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
-
- Moriyama EH, Zheng G and Wilson BC (2008) Optical molecular imaging: From single cell to patient. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther 84, 267–271. - PubMed
-
- Yu J, Xiao J, Ren XJ, Lao KQ and Xie XS (2006) Probing gene expression in live cells, one protein molecule at a time. Science 311, 1600–1603. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

