Elevated expression of caspase-3 inhibitors, survivin and xIAP correlates with low levels of apoptosis in active rheumatoid synovium
- PMID: 19171073
- PMCID: PMC2688245
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2603
Elevated expression of caspase-3 inhibitors, survivin and xIAP correlates with low levels of apoptosis in active rheumatoid synovium
Abstract
Introduction: Tumour necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is a tumour necrosis factor (TNF) family member capable of inducing apoptosis in many cell types.
Methods: Using immunohistochemistry, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase biotin-dUTP nick end labelling (TUNEL) and real-time PCR we investigated the expression of TRAIL, TRAIL receptors and several key molecules of the intracellular apoptotic pathway in human synovial tissues from various types of arthritis and normal controls. Synovial tissues from patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA), inactive RA, osteoarthritis (OA) or spondyloarthritis (SpA) and normal individuals were studied.
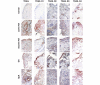
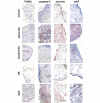
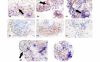
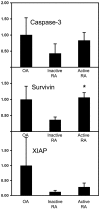
Results: Significantly higher levels of TRAIL, TRAIL R1, TRAIL R2 and TRAIL R4 were observed in synovial tissues from patients with active RA compared with normal controls (p < 0.05). TRAIL, TRAIL R1 and TRAIL R4 were expressed by many of the cells expressing CD68 (macrophages). Lower levels of TUNEL but higher levels of cleaved caspase-3 staining were detected in tissue from active RA compared with inactive RA patients (p < 0.05). Higher levels of survivin and x-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (xIAP) were expressed in active RA synovial tissues compared with inactive RA observed at both the protein and mRNA levels.
Conclusions: This study indicates that the induction of apoptosis in active RA synovial tissues is inhibited despite stimulation of the intracellular pathway(s) that lead to apoptosis. This inhibition of apoptosis was observed downstream of caspase-3 and may involve the caspase-3 inhibitors, survivin and xIAP.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of apoptosis in periodontitis.J Dent Res. 2010 Jan;89(1):29-33. doi: 10.1177/0022034509350708. J Dent Res. 2010. PMID: 19948942
-
Rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid macrophages express decreased tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand R2 and increased decoy receptor tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand R3.Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Nov;48(11):3096-101. doi: 10.1002/art.11302. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. PMID: 14613271
-
Actinomycin D renders cultured synovial fibroblasts susceptible to tumour necrosis factor related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis.Scand J Rheumatol. 2003;32(6):356-63. doi: 10.1080/03009740410005025. Scand J Rheumatol. 2003. PMID: 15080267
-
The two directions of TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in rheumatoid arthritis.Cytokine. 2013 Aug;63(2):81-90. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2013.04.011. Epub 2013 May 4. Cytokine. 2013. PMID: 23651570 Review.
-
Down-regulation of intracellular anti-apoptotic proteins, particularly c-FLIP by therapeutic agents; the novel view to overcome resistance to TRAIL.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Oct;233(10):6470-6485. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26585. Epub 2018 May 9. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29741767 Review.
Cited by
-
miR-431-5p regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis in fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis by targeting XIAP.Arthritis Res Ther. 2020 Oct 6;22(1):231. doi: 10.1186/s13075-020-02328-3. Arthritis Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 33023644 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of 17β estradiol on blood pressure elevation in ovariectomized rats with collagen-induced arthritis via modulation of oxidative stress, inflammation, fibrosis, and apoptosis in the aorta involving TLR4/NOX4/NF-kβ and TGFβ1/fibronectin/α-SMA pathways.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jun;398(6):6941-6962. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03700-9. Epub 2024 Dec 19. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39702602
-
Intracellular apoptotic pathways: a potential target for reducing joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis.Inflamm Res. 2018 Mar;67(3):219-231. doi: 10.1007/s00011-017-1116-5. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Inflamm Res. 2018. PMID: 29164267 Review.
-
XAF1 promotes osteoclast apoptosis by antagonizing the XIAP-caspase axis.J Orthop Translat. 2024 Jun 7;47:15-28. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2024.05.001. eCollection 2024 Jul. J Orthop Translat. 2024. PMID: 38957269 Free PMC article.
-
Cell death in chronic inflammation: breaking the cycle to treat rheumatic disease.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020 Sep;16(9):496-513. doi: 10.1038/s41584-020-0455-8. Epub 2020 Jul 8. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32641743 Review.
References
-
- Hsu HC, Wu Y, Mountz JD. Tumor necrosis factor ligand-receptor superfamily and arthritis. Curr Dir Autoimmun. 2006;9:37–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

