Sequential intravesical gemcitabine and mitomycin C chemotherapy regimen in patients with non-muscle invasive bladder cancer
- PMID: 19171491
- PMCID: PMC3565601
- DOI: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2008.11.019
Sequential intravesical gemcitabine and mitomycin C chemotherapy regimen in patients with non-muscle invasive bladder cancer
Abstract
Objectives: Currently, there are few options other than cystectomy for the management of BCG refractory non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. We report our experience with intravesical combination chemotherapy using gemcitabine and MMC in such patients.
Materials and methods: We identified all patients with non-muscle invasive bladder cancer who were BCG refractory or intolerant and had been treated with intravesical gemcitabine and MMC at our institution. Patients were treated with a combination of intravesical gemcitabine (1000 mg in 50 ml sterile water) followed sequentially by intravesical MMC (40 mg in 20 ml sterile water) every week for 6 weeks (induction). Induction therapy was followed by a maintenance regimen using the same dose of gemcitabine and MMC once a month for 12 months. Data regarding patient demographics and disease information such as previous intravesical therapy, previous cystoscopy, cytology results, time to recurrence, and side effect profile were collected.
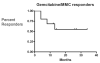
Results: A total of 10 patients (6 male and 4 female) aged 48 to 85 years (median 67 years) underwent treatment with a median follow-up of 26.5 months (4-34 months). Six patients were recurrence free and have maintained their response at a median of 14 months (4-34 months). Four patients had biopsy proven recurrence. Median time to recurrence was 6 months (range 4-13 months). The therapy was well tolerated in all patients. There were no major complications. Two patients experienced irritative lower urinary tract symptoms, which did not require cessation of therapy and one experienced a maculopapillary rash that improved with benadryl.
Conclusions: In patients with recurrent BCG refractory bladder cancer, intravesical combination chemotherapy with gemcitabine and MMC appears to be well tolerated and yields a response in a good proportion number of patients.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multi-institutional analysis of sequential intravesical gemcitabine and mitomycin C chemotherapy for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer.Urol Oncol. 2014 Jan;32(1):35.e15-9. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2013.01.009. Epub 2013 Mar 17. Urol Oncol. 2014. PMID: 23510863 Free PMC article.
-
Intravesical gemcitabine in combination with mitomycin C as salvage treatment in recurrent non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer.BJU Int. 2016 Mar;117(3):456-62. doi: 10.1111/bju.13088. Epub 2015 May 23. BJU Int. 2016. PMID: 25682834
-
A Phase I Trial of Intravesical Cabazitaxel, Gemcitabine and Cisplatin for the Treatment of Nonmuscle Invasive bacillus Calmette-Guérin Unresponsive or Recurrent/Relapsing Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder.J Urol. 2020 Aug;204(2):247-253. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000000919. Epub 2020 Mar 2. J Urol. 2020. PMID: 32118506 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Intravesical gemcitabine versus mitomycin for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial.BMC Urol. 2020 Jul 13;20(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s12894-020-00610-9. BMC Urol. 2020. PMID: 32660456 Free PMC article.
-
Experience with Sequential Intravesical Gemcitabine and Docetaxel as Salvage Therapy for Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer.Curr Urol Rep. 2016 May;17(5):38. doi: 10.1007/s11934-016-0594-2. Curr Urol Rep. 2016. PMID: 26968418 Review.
Cited by
-
Current Clinical Trials in Non-muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: Heightened Need in an Era of Chronic BCG Shortage.Curr Urol Rep. 2019 Nov 28;20(12):84. doi: 10.1007/s11934-019-0952-y. Curr Urol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31781942 Review.
-
Solubilization and Stability of Mitomycin C Solutions Prepared for Intravesical Administration.Drugs R D. 2017 Jun;17(2):297-304. doi: 10.1007/s40268-017-0183-y. Drugs R D. 2017. PMID: 28470465 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-institutional analysis of sequential intravesical gemcitabine and mitomycin C chemotherapy for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer.Urol Oncol. 2014 Jan;32(1):35.e15-9. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2013.01.009. Epub 2013 Mar 17. Urol Oncol. 2014. PMID: 23510863 Free PMC article.
-
Intravesical docetaxel for high-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer after Bacillus Calmette-Guérin failure.Curr Urol. 2021 Mar;15(1):33-38. doi: 10.1097/CU9.0000000000000010. Epub 2021 Mar 29. Curr Urol. 2021. PMID: 34084119 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Combination Therapies for the Treatment of Bladder Cancer.Front Oncol. 2021 Jan 27;10:539527. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.539527. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33585182 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jemal A, Clegg LX, Ward E, et al. Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975–2001, with a special feature regarding survival. Cancer. 2004;101:3–27. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58:71–96. - PubMed
-
- Lamm DL, Blumenstein BA, Crawford ED, et al. A randomized trial of intravesical doxorubicin and immunotherapy with bacille Calmette-Guerin for transitional-cell carcinoma of the bladder. N Engl J Med. 1991;325:1205–9. - PubMed
-
- Joudi FN, O’Donnell MA. Second-line intravesical therapy vs. cystectomy for bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) failures. Curr Opin Urol. 2004;14:271–5. - PubMed
-
- Huncharek M, Kupelnick B. Impact of intravesical chemotherapy vs. BCG immunotherapy on recurrence of superficial transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder: Meta-analytic re-evaluation. Am J Clin Oncol. 2003;26:402–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical