Divergent regulation of cardiac KCND3 potassium channel expression by the thyroid hormone receptors alpha1 and beta1
- PMID: 19171649
- PMCID: PMC2675000
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.168385
Divergent regulation of cardiac KCND3 potassium channel expression by the thyroid hormone receptors alpha1 and beta1
Abstract
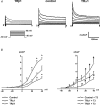
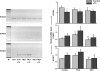
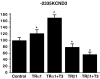
The cardiac transient outward current I(to) is regulated by thyroid hormone (T3). However, it remains unclear whether T3 directly modulates underlying gene transcription and which thyroid receptor (TR) isoform might be responsible for gene transactivation. To clarify this situation, we analysed the role of T3 and its receptors alpha1 (TRalpha1) and beta1 (TRbeta1) in regulation of KCNA4, KCND2, KCND3 and KCNIP2 transcription in rat cardiomyocytes. Initial results demonstrated a T3-mediated increase of I(to) current density. T3 stimulation enhanced KCND2 and KCND3 expression and decreased KCNA4 transcription, while KCNIP2 remained unaffected. To dissect the role of TRalpha1 and TRbeta1 in T3-dependent I(to) modulation, TRalpha1 and TRbeta1 were overexpressed in cardiomyocytes by adenovirus-mediated gene transfer. TRalpha1 increased I(to), while TRbeta1 significantly reduced I(to) in size, which was associated with TRalpha1-mediated increase and TRbeta1-mediated reduction of KCND2/3 transcription. To further evaluate a possible direct interaction of TRalpha1 and TRbeta1 with the KCND3 promoter, TR expression vectors were cotransfected with a construct containing 2335 bp of the KCND3 5'-flanking sequence linked to a luciferase reporter into ventricular myocytes. While the TRalpha1 aporeceptor enhanced KCND3 transcription, the TRbeta1 aporeceptor suppressed KCND3 expression, with both effects exhibiting ligand-dependent amplification upon T3 stimulation. Deletion of the KCND3 5'-flanking region localized the suppressible promoter sequence for TRbeta1 to within -293 bp and the activating promoter sequence for TRalpha1 to within -2335 to -1654 bp of the transcription start site. Disruption of putative TR binding sites by mutagenesis abolished the TRalpha1- (G-1651T) and TRbeta1- (G-73T) mediated effects, indicating that TRalpha1 and TRbeta1 response elements map to different regions of the KCND3 promoter. Thus, I(to) is modulated by diverse T3-dependent regulation of underlying gene transcription. TRalpha1 and TRbeta1 exhibit distinct effects on KCND3 transactivation with TRalpha1 enhancing and TRbeta1 suppressing KCND3 transcription.
Figures

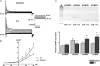
Similar articles
-
Ligand-mediated decrease of thyroid hormone receptor-alpha1 in cardiomyocytes by proteosome-dependent degradation and altered mRNA stability.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005 Feb;288(2):H813-21. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00804.2004. Epub 2004 Oct 21. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15498821
-
Expression pattern and ontogenesis of thyroid hormone receptor isoforms in the mouse heart.J Endocrinol. 2006 May;189(2):231-45. doi: 10.1677/joe.1.06282. J Endocrinol. 2006. PMID: 16648291
-
Thyroid hormone receptor function in maturing ovine cardiomyocytes.J Physiol. 2019 Apr;597(8):2163-2176. doi: 10.1113/JP276874. Epub 2019 Mar 20. J Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30770568 Free PMC article.
-
The thyrotropin-releasing hormone gene 1998: cloning, characterization, and transcriptional regulation in the central nervous system, heart, and testis.Thyroid. 1998 Oct;8(10):897-901. doi: 10.1089/thy.1998.8.897. Thyroid. 1998. PMID: 9827656 Review.
-
Thyroid hormones, t3 and t4, in the brain.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014 Mar 31;5:40. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2014.00040. eCollection 2014. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014. PMID: 24744751 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Whole-genome sequencing reveals genetic structure and adaptive genes in Nepalese buffalo breeds.BMC Genomics. 2024 Nov 14;25(1):1082. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10993-w. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39543523 Free PMC article.
-
MuRF1 mono-ubiquitinates TRα to inhibit T3-induced cardiac hypertrophy in vivo.J Mol Endocrinol. 2016 Apr;56(3):273-90. doi: 10.1530/JME-15-0283. Epub 2016 Feb 9. J Mol Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 26862156 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct regulation of cardiac I(f) current via thyroid receptors alpha1 and beta1.Pflugers Arch. 2009 Oct;458(6):1061-8. doi: 10.1007/s00424-009-0691-x. Epub 2009 Jul 22. Pflugers Arch. 2009. PMID: 19629520
-
Long-term contractile activity and thyroid hormone supplementation produce engineered rat myocardium with adult-like structure and function.Acta Biomater. 2018 Sep 15;78:98-110. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.08.003. Epub 2018 Aug 4. Acta Biomater. 2018. PMID: 30086384 Free PMC article.
-
Thyroid hormone receptor-α and vascular function.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012 May 1;302(9):C1346-52. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00292.2011. Epub 2012 Feb 8. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22322976 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basset A, Blanc J, Messas E, Hagege A, Elghozi JL. Renin-angiotensin system contribution to cardiac hypertrophy in experimental hyperthyroidism: an echocardiographic study. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2001;37:163–172. - PubMed
-
- Beuckelmann DJ, Nabauer M, Erdmann E. Alterations of K+ currents in isolated human ventricular myocytes from patients with terminal heart failure. Circ Res. 1993;73:379–385. - PubMed
-
- Cheng SY. Multiple mechanisms for regulation of the transcriptional activity of thyroid hormone receptors. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2000;1:9–18. - PubMed
-
- Desvergne B. How do thyroid hormone receptors bind to structurally diverse response elements? Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1994;100:125–131. - PubMed
-
- Dixon JE, Shi W, Wang H, McDonald C, Yu H, Wymore RS, Cohen IS, McKinnon D. Role of the Kv4.3 K+ channel in ventricular muscle. A molecular correlate for the transient outward current. Circ Res. 1996;79:659–668. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

