Differential DNA damage signaling accounts for distinct neural apoptotic responses in ATLD and NBS
- PMID: 19171781
- PMCID: PMC2648541
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1746609
Differential DNA damage signaling accounts for distinct neural apoptotic responses in ATLD and NBS
Abstract
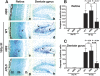
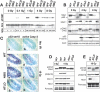
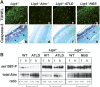
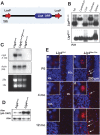
The MRN complex (Mre11/RAD50/NBS1) and ATM (ataxia telangiectasia, mutated) are critical for the cellular response to DNA damage. ATM disruption causes ataxia telangiectasia (A-T), while MRN dysfunction can lead to A-T-like disease (ATLD) or Nijmegen breakage syndrome (NBS). Neuropathology is a hallmark of these diseases, whereby neurodegeneration occurs in A-T and ATLD while microcephaly characterizes NBS. To understand the contrasting neuropathology resulting from Mre11 or Nbs1 hypomorphic mutations, we analyzed neural tissue from Mre11(ATLD1/ATLD1) and Nbs1(DeltaB/DeltaB) mice after genotoxic stress. We found a pronounced resistance to DNA damage-induced apoptosis after ionizing radiation or DNA ligase IV (Lig4) loss in the Mre11(ATLD1/ATLD1) nervous system that was associated with defective Atm activation and phosphorylation of its substrates Chk2 and p53. Conversely, DNA damage-induced Atm phosphorylation was defective in Nbs1(DeltaB/DeltaB) neural tissue, although apoptosis occurred normally. We also conditionally disrupted Lig4 throughout the nervous system using Nestin-cre (Lig4(Nes-Cre)), and while viable, these mice showed pronounced microcephaly and a prominent age-related accumulation of DNA damage throughout the brain. Either Atm-/- or Mre11(ATLD1/ATLD1) genetic backgrounds, but not Nbs1(DeltaB/DeltaB), rescued Lig4(Nes-Cre) microcephaly. Thus, DNA damage signaling in the nervous system is different between ATLD and NBS and likely explains their respective neuropathology.
Figures

References
-
- Ahn J.Y., Schwarz J.K., Piwnica-Worms H., Canman C.E. Threonine 68 phosphorylation by ataxia telangiectasia mutated is required for efficient activation of Chk2 in response to ionizing radiation. Cancer Res. 2000;60:5934–5936. - PubMed
-
- Barnes D.E., Stamp G., Rosewell I., Denzel A., Lindahl T. Targeted disruption of the gene encoding DNA ligase IV leads to lethality in embryonic mice. Curr. Biol. 1998;8:1395–1398. - PubMed
-
- Bredemeyer A.L., Sharma G.G., Huang C.Y., Helmink B.A., Walker L.M., Khor K.C., Nuskey B., Sullivan K.E., Pandita T.K., Bassing C.H., et al. ATM stabilizes DNA double-strand-break complexes during V(D)J recombination. Nature. 2006;442:466–470. - PubMed
-
- Callen E., Jankovic M., Difilippantonio S., Daniel J.A., Chen H.T., Celeste A., Pellegrini M., McBride K., Wangsa D., Bredemeyer A.L., et al. ATM prevents the persistence and propagation of chromosome breaks in lymphocytes. Cell. 2007;130:63–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
