Waiting list mortality among children listed for heart transplantation in the United States
- PMID: 19171850
- PMCID: PMC4278666
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.815712
Waiting list mortality among children listed for heart transplantation in the United States
Abstract
Background: Children listed for heart transplantation face the highest waiting list mortality in solid-organ transplantation medicine. We examined waiting list mortality since the pediatric heart allocation system was revised in 1999 to determine whether the revised allocation system is prioritizing patients optimally and to identify specific high-risk populations that may benefit from emerging pediatric cardiac assist devices.
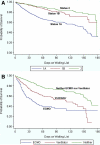
Methods and results: We conducted a multicenter cohort study using the US Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients. All children <18 years of age who were listed for a heart transplant between 1999 and 2006 were included. Among 3098 children, the median age was 2 years (interquartile range 0.3 to 12 years), and median weight was 12.3 kg (interquartile range 5 to 38 kg); 1294 (42%) were nonwhite; and 1874 (60%) were listed as status 1A (of whom 30% were ventilated and 18% were on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation). Overall, 533 (17%) died, 1943 (63%) received transplants, and 252 (8%) recovered; 370 (12%) remained listed. Multivariate predictors of waiting list mortality include extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support (hazard ratio [HR] 3.1, 95% confidence interval [CI] 2.4 to 3.9), ventilator support (HR 1.9, 95% CI 1.6 to 2.4), listing status 1A (HR 2.2, 95% CI 1.7 to 2.7), congenital heart disease (HR 2.2, 95% CI 1.8 to 2.6), dialysis support (HR 1.9, 95% CI 1.2 to 3.0), and nonwhite race/ethnicity (HR 1.7, 95% CI 1.4 to 2.0).
Conclusions: US waiting list mortality for pediatric heart transplantation remains unacceptably high in the current era. Specific high-risk subgroups can be identified that may benefit from emerging pediatric cardiac assist technologies. The current pediatric heart-allocation system captures medical urgency poorly. Further research is needed to define the optimal organ-allocation system for pediatric heart transplantation.
Figures




References
-
- McDiarmid S. Death on the pediatric waiting list: scope of the problem.. Paper presented at: Summit on Organ Donation and Transplantation; San Antonio, Tex.. March 2007.
-
- Renlund DG, Taylor DO, Kfoury AG, Shaddy RS. New UNOS rules: historical background and implications for transplantation management: United Network for Organ Sharing. J Heart Lung Transplant. 1999;18:1065–1070. - PubMed
-
- West LJ, Pollock-Barziv SM, Dipchand AI, Lee KJ, Cardella CJ, Benson LN, Rebeyka IM, Coles JG. ABO-incompatible heart transplantation in infants. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:793–800. - PubMed
-
- West LJ, Karamlou T, Dipchand AI, Pollock-BarZiv SM, Coles JG, McCrindle BW. Impact on outcomes after listing and transplantation, of a strategy to accept ABO blood group-incompatible donor hearts for neonates and infants. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2006;131:455–461. - PubMed
-
- Addonizio LJ, Naftel D, Fricker J, Morrow WR, Kirklin JK, McGiffin DC, Dodd D, Bernstein D. Risk factors for pretransplant outcome in children listed for cardiac transplantation: a multi-institutional study. J Heart Lung Transplant. 1995;14:S48. Abstract.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

